Role of Procurement Automation in Efficient Business Operations


Cflow Team
Share this Content
Manual procurement processes are costing organizations more than they realize. Delayed approvals, processing errors, and limited spend visibility create operational inefficiencies that compound across departments and suppliers.
Modern businesses are turning to procurement automation to address these challenges systematically. By replacing manual workflows with intelligent, automated systems, companies are achieving measurable improvements in cycle times, cost control, and compliance management.
This comprehensive guide examines how procurement automation works, its key benefits, and proven implementation strategies that deliver sustainable results.
Table of Contents
What is Procurement Automation?
Procurement automation is simply the use of technology to optimize and manage the procurement process, replacing repetitive, low-value manual tasks with automated workflows. It allows organizations to process requests, approve requisitions and orders, make payments, and perform other related duties mostly without human touch, thus generating faster cycles, reduced costs, and errors.
Practically speaking, procurement automation entails using software solutions to eliminate low-value activities like approving purchase requisitions and onboarding suppliers, matching invoices, and tracking orders. By removing these standard steps from manual work and converting them to automated workflows, you can increase cycle time, compliance, and visibility to spending in real-time.
Understanding the Procurement Processes
The procurement function is an essential part of every business, irrespective of the size or type of the business. The procurement function is made up of a series of steps that are performed by an organization to obtain goods or services that are required to achieve business goals and objectives. Identifying and working with the best suppliers to obtain goods or services at the best prices and of good quality is the aim of the procurement function.
The output of the procurement function has a direct bearing on the cost-saving initiatives of the organization. In addition to cost-saving objectives, the procurement function also focuses on risk and compliance management, improving supplier performance, shortening the sourcing cycle time, and improving contract utilization.
An effective procurement process focuses beyond just the purchase of goods and services. Gaining a complete understanding of the requirements of all business units, mapping the right supplier with the requirement, monitoring and evaluating vendor performance, and negotiating contracts to derive value for money are some of the main focus areas of the procurement function.
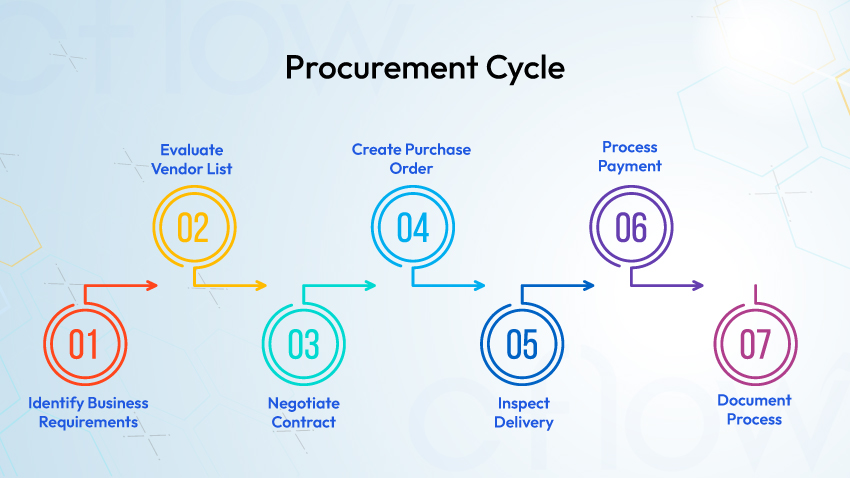
7 Important Steps to an Effective Procurement Function:
A structured procurement process ensures cost efficiency, compliance, and smooth supplier relationships from requirement gathering to final payment.
1. Identify and understand the business requirements of all business units
A job well begun is half done. Understanding the business requirements of individual business units is the most effective start to the procurement function. Identifying and consolidating the requirements of all business units provides visibility into the categorical spending and cost-saving areas in the organization.
2. Identify and evaluate the vendor list
Once the requirements are identified and consolidated, the search for relevant suppliers begins. Vendor search may be conducted online or through more structured searches like RFPs, FFIs, and RFQs. The identified vendors are evaluated based on their pricing, track record, warranty, and guarantee terms, industry recognitions, and quality of service. The vendor offering the best market price and the maximum value is chosen by the procurement team.
3. Contract negotiation with the chosen vendor
Once the vendor is chosen by the business, the contract negotiation process begins. Contract negotiation is an important step in the purchasing process. The buyer-supplier relationship and value creation for the purchase can be improved through tactical contract negotiation. Scope of work, pricing structure, discounts, delivery timelines, and terms and conditions are the factors asserted while negotiating the contract.
4. Create and submit a Purchase requisition and release the Purchase Order
The Finalization of the vendor contract leads to the next step in the purchasing process, which is the creation and submission of the purchase requisition (PR). All the contract terms that are mutually agreed upon are mentioned in the purchase requisition.
The PR is submitted for approval by the procurement head and the finance. Once it is approved by the finance, a purchase order (PO) is raised by the finance team to the supplier containing information such as the purchase order number, supplier information, and pricing and delivery time.
5. Receive and Inspect the Goods and Services upon delivery
The vendor delivers goods and services against the purchase order. The procurement team needs to inspect the delivery to ascertain the quality of the goods or services delivered. Successful delivery inspection will initiate payment for the order, while failed inspection leads to rejection and return of goods and services.
6. Process the payment to the vendor against the invoice
Most suppliers send the invoice for payment, mentioning the price for the delivered goods/services at the time of delivery. The procurement team matches the PO against the invoice to ensure that the quality and quantity of the purchase are met. The payment of the invoice may be pre- or post-delivery according to the terms agreed by the supplier and buyer.
7. Document the purchase process
Once the purchase process is complete, end-to-end documentation of the purchase-to-pay cycle is required. Documentation helps track and analyze the expenditure and ensures audit readiness of the procurement process.
Each of the above steps can be customized according to organizational needs.
If you’d like to explore procurement automation concepts in more detail, you can also check out this in-depth guide on procurement automation for additional insights and practical applications.
| Aspect | Procurement Digitization | Procurement Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting paper-based processes into digital document formats, such as replacing paper purchase orders with PDFs. | Using technology to not only digitize documents but also orchestrate the full procurement process automatically. |
| Scope | Focuses on document conversion and storage. | Covers end-to-end workflows, from requisition to payment, with built-in rules and routing. |
| Capabilities | Creates digital versions of documents for easier storage and sharing. | Triggers actions and alerts, enforces policies, and integrates with finance or ERP systems. |
| Human Involvement | Requires manual follow-up for approvals and process progression. | Minimizes human intervention by automating tasks and approvals. |
Challenges of Manual Procurement Processing
Manual procurement is slow, error-prone, and resource-heavy, creating delays and risks across the procure-to-pay cycle. It leads to:
Compliance and risk issues – Limited visibility and human bias increase exposure to market, delivery, and operational risks. Fraud, policy breaches, and inaccurate records become harder to detect.
Uncontrolled spending – Off-contract purchases and untracked indirect spending inflate costs and weaken budget control.
Slow process cycles – Manual routing of PRs, POs, and invoices causes delays, repetitive admin work, and missed chances for early payment discounts.
Data errors – Manual entry and scattered records lead to reporting mistakes, poor forecasting, and bad purchasing decisions.
Too much paperwork – Paper invoices and approvals are hard to manage, easy to lose, and slow to retrieve for audits.
Poor vendor management – Delayed approvals, missed payments, and inconsistent communication damage supplier relationships and reduce negotiation power.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
5 Procurement Processes Ideal for Automation
These processes are high-impact areas where automation delivers the fastest efficiency gains, cost savings, and compliance improvements in procurement.
1. Purchase Requisitions and Purchase Orders
Approval delays for PRs and POs slow procurement. Automation speeds up reviews with instant notifications, tracks approval status, and generates digital purchase orders once approved, improving visibility and reducing bottlenecks.
2. Invoice Management and Payment Processing
Manual invoice matching is prone to errors and delays. Automated systems digitize data, match invoices against POs and receipts, and process payments quickly from accounts payable, eliminating missed payments and creating a clear audit trail.
3. Vendor Management and Sourcing
Automation centralizes supplier data, including qualifications, performance metrics, compliance status, location, and ESG practices. This real-time access helps procurement managers make informed sourcing decisions faster.
4. Contract Management
Automated contract systems track lifecycles, monitor compliance, and send renewal alerts. A centralized, searchable repository improves transparency and ensures stakeholders act before deadlines.
5. Spend Analysis
Procurement strategies rely on accurate spend insights. Automation accelerates data analysis, identifies cost-saving opportunities, and highlights supplier performance trends with greater accuracy.
| Aspect | Manual Procurement | Automated Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| Process Flow | Approvals and purchase orders move between multiple inboxes, spreadsheets, and paper files. | Requests are routed automatically through a centralized system. |
| Efficiency | Prone to delays, bottlenecks, and disruptions. | Provides structure, standardization, and faster processing. |
| Risk | Higher chance of errors, miscommunication, and non-compliance. | Enforces compliance, tracks performance, and minimizes risk. |
| Sustainability and Ethics | Difficult to track sustainable or ethical sourcing consistently. | Built-in tools for responsible sourcing and compliance with sustainability goals. |
Components and Workflow of Procurement Automation
Procurement automation uses digital technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and robotic process automation (RPA) to optimize the entire procurement lifecycle.
It eliminates repetitive manual tasks, reduces human error, enhances visibility, and accelerates purchasing. More than just automating transactions, it adds intelligence and adaptability to sourcing, contract management, supplier collaboration, and spend control.
An automated procurement system typically covers these key components across the source-to-pay (S2P) cycle:
1. Automated Purchase Requisitions
Employees create purchase requests via a self-service portal with pre-approved catalogs, supplier options, and pricing. Requests are routed automatically based on approval hierarchies, budget limits, or department codes.
2. Digital Approval Workflows
Pre-set rules send requisitions, purchase orders (POs), and invoices to the right stakeholders for approval. Approvers can respond via email, mobile, or dashboards, reducing delays and ensuring compliance.
3. Automated Sourcing and Supplier Management
From RFPs and RFQs to onboarding, suppliers submit documents through secure portals, with the system auto-verifying details against policies or external databases. Supplier performance metrics and risk ratings are updated in real time.
4. Purchase Order Creation and Distribution
Once approved, the system generates a PO with supplier details, pricing, delivery timelines, and terms, sending it electronically for confirmation.
5. Goods Receipt and Tracking
Upon delivery, goods are confirmed against the PO through barcode scanning or digital acknowledgment. Automated alerts flag late, incomplete, or damaged shipments.
6. Three-Way Matching and Invoice Processing
The system matches the PO, goods receipt, and invoice before approving payment. Discrepancies trigger alerts for review, reducing errors and fraud risk.
7. Automated Payment Processing
Approved invoices trigger payments according to agreed terms, with early payment discounts applied where possible. Payment methods like ACH or virtual cards are executed automatically, ensuring accurate records and audit trails.
8. Contract Lifecycle Management
Contracts are digitized, searchable, and linked to POs and invoices. The system sends renewal alerts, tracks compliance, and helps legal teams draft agreements with pre-approved clauses.
9. Spend Analytics and Reporting
Real-time dashboards consolidate spend data by supplier, category, or region. AI-driven insights help detect anomalies, forecast demand, and identify savings opportunities.
10. Compliance Monitoring and Policy Enforcement
Embedded rules block non-compliant purchases and enforce approval requirements. Detailed audit logs ensure transparency for internal and external reviews.
11. ERP and Financial System Integration
Seamless integration with ERP, accounts payable, CRM, and inventory systems ensures accurate data flow across business units and aligns procurement with budgeting and forecasting.
Advantages of Procurement Automation
For Procurement Teams
Accelerates the approval process
Typical delays in the procurement process are during PR or PO, or invoice approvals. Automating the PO or PR approval process enables quick placement of orders and cuts down the ordering cycle time as well.
Streamlines spend management
Procurement automation provides visibility into historical spending. The software provides updates on past purchases, contract statuses, order history, and supplier quotes. Workflow automation provides a consolidated view of the actual expenses that are useful in making data-driven management decisions.
For Finance Teams
Provides a centralized data repository
The terms and conditions for contracts remain the same across multiple suppliers. Automated procurement software enables centralized access to all contracts and other critical data. Centralized data access ensures that T&C and guidelines are uniform across all the contracts.
Improves overall productivity
Automation takes care of the repetitive and redundant tasks in the procurement workflow. Employees are freed from these tasks and get time to focus on strategic initiatives. Employees can easily access information without having to navigate through multiple systems. Procurement automation not only increases efficiency but also provides complete control of the procurement cycle.
For Suppliers
Promotes trust and reliability in supplier relationships
Establishing long-term supplier relationships requires transparency and a clear line of disclosure. Procurement automation helps establish clear real-time communication between buyer and supplier, which enables easy tracking of order status, time and cost savings, and fast grievance resolution.
Responsiveness is high in an automated purchasing system, which enables buyers to assign the order to the best quote and suppliers to quickly respond to the bids.
Also Read: 3 things to improve professional performance
Industry-Specific Uses for Procurement Automation
Procurement automation produces quantifiable benefits in many industries. Customized workflows designed for specific industries allow organizations the opportunity to improve productivity, compliance, and supplier cooperation.
1. Manufacturing
Automation smooths the sourcing of raw materials, purchase order approvals, and supplier performance metrics. Connect these elements with inventory in real-time, maintain production schedules, and minimize the chances of stock-outs or excess stock.
2. Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare supply companies leverage automation for medical equipment orders, vendor compliance with safety protocols, and timely orders for critical supplies. Compliance upholds patient safety, and timely orders reduce costs.
3. Retail
Retailers automate ordering for replenishment cycles, plan seasonal orders, and coordinate vendor activities for promotions, resulting in improved inventory availability and quicker response to market needs.
4. Public Sector
Governmental agencies utilize procurement automation to manage rigid compliance requirements, oversee vendor contracts, and streamline the tendering process, minimizing delays to the delivery of public services.
5. Technology & Services
Technology and service-based companies utilize automation to manage renewing contracts, buy software licenses, and onboard vendors, to improve operational agility and reduce administrative burden.
Key Statistics on Procurement Automation Impact
Key statistics of procurement automation highlight significant benefits in efficiency, cost savings, accuracy, compliance, and data-driven decision-making:
Technology Investment Trends: 55% of companies plan increased supply chain technology investment in 2024, emphasizing automation and analytics as key focus areas (MHI and Deloitte, The Hackett Group).
Operational Cost Reduction: Automated procurement processes can reduce operational costs by 30-50% compared to manual processes (McKinsey & Company).
Time Savings: Organizations can cut procurement cycle times by up to 50% through automation (Deloitte).
Error Reduction: Manual data entry has error rates of 1-5%; automation significantly minimizes these errors, increasing accuracy up to 40-45%.
Audit and Compliance Improvement: Automation reduces risk of non-compliance penalties by up to 55% by ensuring adherence to regulations and providing clear audit trails (Gartner).
Fraud Prevention: Automated data monitoring reduces procurement fraud losses by 52% compared to non-automated processes (Association of Certified Fraud Examiners).
Supplier Onboarding Time: Digital procurement cuts onboarding time by up to 70% (Association of Certified Fraud Examiners).
Supplier Performance Monitoring: Automation can improve supplier compliance rates by 30-40% due to continuous performance tracking (PwC).
Spend Visibility: Organizations with automated procurement report up to 80% greater visibility into spending data, enabling better budget management (Forrester Research).
Cost Savings on Spend: Automation can save companies between 5% and 15% on procurement spending through improved analysis and sourcing (The Hackett Group).
User Adoption: User-friendly procurement automation systems can increase adoption rates by 60%, improving productivity (Spend Matters).
Real-world Impact: IBM saved $100 million annually, and Cisco reduced procurement cycle times by 40% after automation implementations.
Evolution of Automation in Procurement
Given the global scale of operations that businesses manage, it becomes extremely important to manage vast amounts of data both within and outside the organization. Proper capture and analysis of spend data helps in identifying spend patterns and market insights. The evolution of procurement automation is mainly driven by the need for effective capture of procurement data.
Early procurement automation practices augmented or replaced manual data entry that was carried out using spreadsheets. Early adoption of procurement automation was dominated by robotic process automation, owing to availability and simple implementation.
Procurement teams used RPA to automate a series of previously manual procurement tasks, like invoice and PO generation and approval. This level of automation required the augmentation of separate software and tools for tasks like contract management or price negotiation.
No code workflow automation tools like Cflow redefined procurement automation by simplifying automation with visual elements as opposed to cumbersome code-based automation. During later years, as machine learning and AI gained prominence, procurement automation implementations revolved around these technologies.
A 2022 IBM survey revealed a sharp increase in the number of businesses adopting procurement automation. Several organizations are using AI to monitor and track performance.
Intelligent Automation in Procurement
Intelligent automation transforms procurement from a rule-based, transactional function into a proactive, insight-driven operation. By combining AI, machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and robotic process automation (RPA), it not only executes tasks but also predicts needs, reduces risks, and drives better decisions.
AI for Decision Support – Analyzes historical spend data, supplier performance, and market trends to recommend the best suppliers, forecast price changes, and determine optimal purchase timing.
ML for Forecasting and Risk Detection – Learns from approval patterns, transaction history, and supplier performance to predict delays, flag anomalies, and uncover hidden inefficiencies in the process.
NLP for Document Intelligence – Extracts and interprets critical terms from contracts, RFPs, and emails, flags non-compliance, and enables users to get instant answers through conversational queries.
RPA for Task Execution – Handles repetitive, high-volume tasks like PO creation, invoice uploads, and data transfers between systems—integrating even with older platforms to maintain process continuity.
Supplier Risk Monitoring – Aggregates internal performance data with external signals like credit ratings, ESG scores, and regulatory alerts to provide real-time supplier risk profiles and automated alerts.
Smart Contract Management – Tracks contract lifecycles, highlights risk clauses, sends renewal reminders, and ensures terms align with actual order and payment data.
Spend Classification and Categorization – Cleans, standardizes, and organizes spend data for accurate reporting, helping identify savings opportunities, tail spend, and vendor consolidation possibilities.
Predictive Procurement Planning – Uses seasonal trends, historical usage, and market conditions to forecast demand, enabling early contract negotiations and avoiding last-minute premium costs.
Virtual Assistants for Operations – AI-powered chatbots guide users in creating requisitions, tracking POs, or accessing supplier updates, improving accessibility and reducing training needs.
When these cognitive technologies are integrated across the source-to-pay cycle, procurement teams gain a connected, data-driven system that delivers efficiency, compliance, and strategic value.
Discover why teams choose Cflow
Implementing Procurement Automation: Steps and Best Practices
Automating the procure-to-pay cycle can transform procurement efficiency, reduce costs, and free employees from repetitive, low-value tasks. Instead of focusing on manual data entry or chasing approvals, teams can dedicate more time to strategic decision-making. Successful implementation requires both a structured rollout and adherence to best practices.
Step 1: Map and Evaluate the Existing Workflow
Start by mapping the current procurement process to gain full visibility into each stage. This helps identify repetitive, error-prone, or time-consuming tasks that are prime candidates for automation. Look for bottlenecks, high-cost stages, and processes that involve large volumes of data entry or validation.
Step 2: Set Clear Goals
Define what you want automation to achieve—shorter approval cycles, improved compliance, lower costs, or better spend visibility. Link these goals to measurable KPIs, such as purchase order cycle time or percentage of spend under management, and ensure they align with broader business priorities.
Step 3: Choose the Right Automation Platform
Select procurement automation software that fits your needs and integrates seamlessly with ERP, finance, or other enterprise systems. Prioritize platforms with low implementation costs, minimal training requirements, mobile accessibility, strong analytics, and vendor support. Cloud-based solutions like Cflow allow anytime, anywhere access.
Step 4: Engage Stakeholders Early
Involve finance, legal, operations, and compliance teams from the outset. Their input ensures workflows address real operational challenges and reduces the risk of adoption resistance later.
Step 5: Standardize Processes
Before building automated workflows, establish standardized procedures for approvals, supplier onboarding, contract management, and invoice matching. Standardization improves compliance, ensures consistency, and accelerates user training.
Step 6: Design and Build Workflows
Use your chosen platform’s workflow builder to create streamlined, automated processes. Treat each procurement task, such as purchase requisitions, invoice approvals, or contract renewals, as an individual workflow. Add conditional routing and approval steps to match business rules.
Step 7: Implement and Test in Phases
Roll out automation gradually rather than all at once. Test each workflow for performance, accuracy, and execution speed before moving to the next stage. This phased approach minimizes disruption and makes it easier to address early issues.
Step 8: Train Users Effectively
Offer role-based training, onboarding sessions, and self-service resources like help centers or in-app guidance. Emphasize not only how to use the system but also the tangible benefits of automation for each role.
Step 9: Monitor, Measure, and Improve
Use analytics dashboards to track KPIs such as cycle time, spend under management, compliance rates, and adoption levels. Conduct periodic reviews to identify bottlenecks and refine workflows for continuous improvement.
Step 10: Ensure Data Security and Compliance
Implement strong governance measures, including access controls, encryption, and audit trails. Work with IT and legal teams to maintain compliance with regulations such as GDPR or ISO 27001 and prepare an incident response plan.
Challenges in Implementing Procurement Automation and How to Overcome Them
While procurement automation offers significant benefits, its success depends on addressing common adoption challenges early.
1. Budget Constraints – Upfront costs for software, integration, and training can delay approval. Build a strong ROI case showing savings from faster approvals, reduced errors, and better compliance. Start with one or two high-impact processes to prove value quickly.
2. Integration Complexity – Connecting automation with ERP, finance, and inventory systems can be challenging, especially with older platforms. Choose software with robust integration features and pre-built connectors, involve IT early, and test integrations in stages.
3. Change Resistance – Employees may worry about new workflows or job changes. Communicate benefits clearly, show how automation removes repetitive tasks, and provide role-specific training.
4. Data Quality Issues – Poor supplier records, outdated contracts, or inconsistent data can limit automation’s effectiveness. Conduct a data audit before rollout and standardize records, templates, and approval hierarchies.
5. Measuring ROI – Without regular tracking, the impact of automation can decline over time. Monitor KPIs such as cycle time, spend under management, and compliance rates, then review results quarterly to refine workflows.
Top 5 Procurement Automation Trends to Watch Out For
Automation and Artificial Intelligence – Machine learning and Intelligent Procurement automation will dominate the scene. Procurement teams should be focusing on adopting Generative AI for advanced analytics. Workflow automation should be adopted for routine tasks in the procurement workflow.
Sustainability will be non-negotiable – ESG (Environmental Social Governance) standards will gain importance, and procurement teams will have to adhere to these standards. Establishing a sustainable business by shifting to greener suppliers and materials will become a must for organizations.
Data-driven procurement with predictive analysis – Procurement functions will shift to predictive spend analytics for optimizing budgets and anticipating purchasing needs. Predictive analytics is required for real-time supplier risk management.
Hyper-personalized and Intelligent procurement platforms – AI-powered customization and end-to-end integration will require hyper-personalization and intelligent procurement platforms. Hyper-personalization is required for faster adaptation to market dynamics and personalization in procurement processes.
Focus on supplier collaboration and innovation – The focus of procurement managers would be more on establishing collaborative supplier ecosystems, real-time supplier performance management, and vendor diversity. Suppliers will be viewed more as partners rather than vendors.
How Cflow Automated Procurement Workflows in SafeSource Direct
SafeSource Direct is a healthcare equipment manufacturer based in the USA. Being a traditionally run business, most of the internal operations in the company were carried out manually. Procurement processes that required approvals were delayed due to manual operations. SafeSource Direct was looking for a procurement automation solution that would relieve them from the manual burden.
By partnering with Cflow, SafeSource Direct was able to digitize the purchase requisition process. Their procurement team was able to fulfill all requests raised across departments by reviewing and approving all requests without any delay or error. Powered by AI-driven workflows in Cflow, SafeSource Direct was able to save a significant amount of time on manual processing.
Conclusion
The question: “Will procurement be automated?” is now replaced with “Which is the best software to automate the procurement function?”. Progressive businesses looking to improve overall productivity are choosing to automate key business process workflows. Cflow makes procurement automation a breeze. Sign up for a free trial today.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is procurement?
Procurement is the process of sourcing, purchasing, and managing goods or services for business needs. Modern organizations use procurement workflow automation to streamline approvals, track spending, and ensure compliance, replacing manual steps with digital processes.
2. What are the 7 steps of procurement?
The 7 steps include identifying needs, selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, creating purchase requisitions, issuing POs, receiving goods, and processing payments. Automated purchasing processes optimize each step for speed, accuracy, and visibility.
3. What are the 4 types of procurement?
The main types are direct procurement, indirect procurement, services procurement, and goods procurement. Procurement workflow automation supports all four by standardizing tasks, reducing errors, and improving supplier collaboration.
4. What is the procurement cycle?
The procurement cycle covers the complete process from identifying needs to payment and record-keeping. With procurement workflow automation, organizations can accelerate each stage, integrate with ERP systems, and improve cost control.
5. What is an RFQ in procurement?
An RFQ (Request for Quotation) invites suppliers to submit pricing for specific goods or services. Automated RFQ management, as part of an automated purchasing process, reduces turnaround times and ensures transparent supplier evaluation.
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business:

Do better workflow automation with Cflow
Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms, etc. to save time and cost.

Talk to a workflow expert
Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize your daily tasks.

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master workflow automation.