Transform Your Business with Influential Business Process Reengineering Examples

Organizations often undergo several drastic changes to shift the dynamics of the workplace, with the focus often being to improve productivity and efficiency. This redesigning and reconstruction of the organizational operations to attain better quality can be put under an approach called Business Process Reengineering (BPR).
Using this approach organizations aim at the complete transformation of the business processes. BPR is a game-changer strategy that paves the way for building a system that helps bring out a business’s complete potential.
Read further to explore more about process reengineering through real-life business process reengineering examples.
What is Business Process Reengineering (BPR)?
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is the complete restructuring of all business operations to attain more efficiency, reduce expenses, and improve the productivity of the business. Most often, a lot of time is wasted when companies try to improve inefficient processes instead of orchestrating something entirely new for the processes.
Business process reengineering, as the name suggests, is a complete formation of new business strategies and the course of action, and hence, it is often considered to be holistic yet uncertain to some extent.
For most organizations, the business processes are still run on traditional technology that is outdated and has several limitations like redundancy, not being able to effectively use human labor, etc. are all downgrading the processes. Business process reengineering can make the processes more efficient by replacing the framework with an updated approach.
How does BPR achieve it? The BPR approach achieves this by analyzing every process and carefully eliminating unnecessary and inefficient parts. An additional functionality that BPR offers is that it will combine similar tasks and drastically reduce the number of steps the employees have to perform. This will achieve two things; first, enhance the employees’ working experience, and second reduce the resources required by the process.
Business Process Reengineering vs. Business Process Improvement
Even though the common goal of both business process reengineering and business process improvement, the results they produce vary in degree. The BPR initiates the complete change of the process, whereas business process improvement is making minor adjustments and smoothening the existing process. Some other differences can be seen on the following grounds:
- Amount of change: BPR results in a more significant and bigger change when compared to BPI.
- Frequency: Business process improvements can be consistently done regularly. On the other hand, BPR is a project-based initiative that changes the foundation dramatically.
- Reasoning: BPR is implemented as a response to changing standards and demand, while a BPI is a preventive strategy.
Importance of Business Process Reengineering
The term became more popular during the 1990s in an article titled “Reengineering Work: Don’t Automate, Obliterate” written by Michael Hammer. He stated:
“Reengineering strives to break away from the old rules about how we organize and conduct business. It involves recognizing and rejecting some of them and then finding imaginative new ways to accomplish work. From our redesigned processes, new rules will emerge that fit the times. Only then can we hope to achieve quantum leaps in performance.”
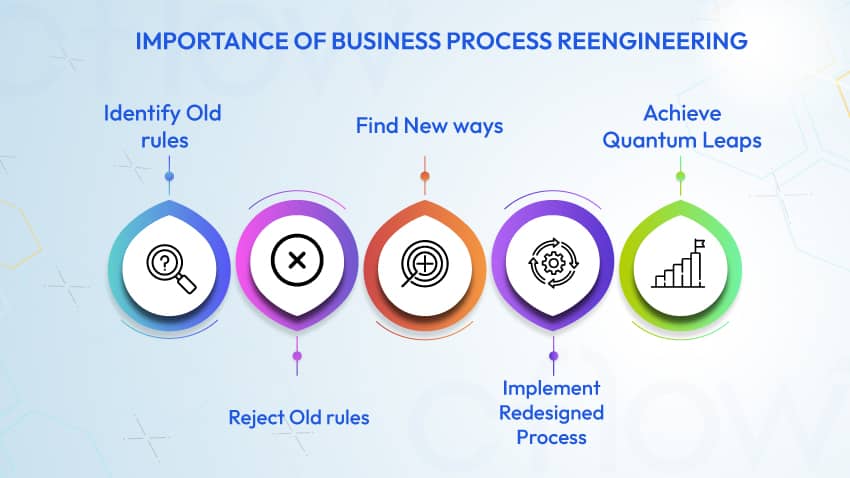
Implementing business process reengineering adds tangible value to the efforts that are put into it if the implementation is done right.
1. Reduced Operational Costs
In a traditional setup, the businesses had to face higher expenditures to meet their expected outcomes and yet remain inefficient. But with business process reengineering, the processes are redesigned, fitting a new framework that requires fewer resources and costs. The BPR takes an approach similar to how we organize personal finances by cutting down on expensive subscriptions. Process reengineering aids in the evaluation of finding such overspending areas and removes those tasks.
2. Drive Higher Profits
The existing workflows of inefficient business operations are completely altered and rightly prioritize efficiency, and productivity, and achieve the desired output. This will completely drive the productivity of the operations and hence attain higher profits.
3. Increase Speed and Efficiency
Business process improvements lead to the enhancement of the speed and efficiency of the process. BPR specifically detects the drawbacks in the existing processes that generally bring down the speed and efficiency of the process. So, once these drawbacks are removed it automatically improves the speed and efficiency of the business processes.
4. Improve the Quality of Products or Services
With improved business processes, employees do not have to focus on burdensome processes. Instead, their complete focus can be given to the betterment of the product or the service. With improvements in process workflow and employee experience, the quality of the product or service increases.
5. Boost Customer Service
Ultimately, with changes made to the inefficient processes, workers’ abilities, and process administration, the service provided will be multiplied in efficiency and effective customer service can be offered.
6. Clarified Purpose
With business process reengineering, there is a re-establishment of organizational goals and the entire team is familiarized with the mission set by the organization. Therefore, the focus of the work is fixed again.
Threats in Business Process Reengineering
Implementing business process reengineering can be significantly impactful and a challenging process as well. Depending on the need, the depth of the impact created can have varied effects on the work dynamics of the organization. Some of the challenges a company would possibly face while implementing BPR are as follows:
Employees Resistance to Change
Sometimes, employees would not be on board with the sudden change, especially when they have been used to doing their work in a certain way for a long period. This can be a cause of concern because if employees are not on the same page as the company’s requirements, the shift cannot be effectively implemented.
Lack of Understanding
Communicating the reasons behind the changes being made is important. Your employees have to understand the necessity and why this is being done. A lack of understanding of the reengineering process can lead to confusion and frustration.
Cost of Implementation
Changing the system of work is expensive as it demands new technology to be implemented, training, and other external resources.
Opportunities in Business Process Reengineering
Even with some threats in place, the opportunities that a business process reengineering offers weigh more in terms of quality of the work and efficiency. Here are some of the three major parameters that improve with a BPR process.
1. Increased Efficiency
Since the processes are streamlined and optimized with the implementation of business process reengineering, businesses can operate more efficiently by reducing resource costs and improving productivity.
2. Improved Quality
The BPR approach would allow organizations to detect and remove inefficiencies and pitfalls in business operations. This will elevate the quality of the service or product provided thus improving customer satisfaction.
3. Competitive Advantage
By achieving process improvement, businesses always have the scope for attaining a competitive edge over the competitors in the industry by providing better products and services at the best price possible.
Seven Business Process Reengineering Steps
There is a set of specific steps to be followed by organizations to have a successful business process reengineering process. Following a standardized process of implementation can offer a seamless shift that will have a minimal impact on the working of the organization. Let us decode the steps.
Step 1: Assemble a BPR Team and Set Goals
If you are looking forward to implementing the BPR solution, it is ideal to assemble a team of experts to carry out the process. The team must have members who have a clear idea of what the processes are and be able to judge them objectively. To achieve this, a three-level group of experts is a must.
-
The Senior Management Team
The senior management team entails the senior managers who are the leaders of this change management. This team will be responsible for strategizing the implementation of the change. They have to make sure that change is being implemented according to the plan in different departments.
Being the leaders of the process, they are also responsible for planning and delegating tasks among the employees. These managers are also required to review and approve the tasks of the change process. Therefore, a clear knowledge of the organization’s processes and the capabilities of the workforce is required to exercise effective decision-making and task assignment.
-
The Operations Managers
Operations managers work under designated teams or processes of the reengineering approach. For instance, in a manufacturing process, the operations manager is designated as the team leader at a specific site. Therefore, the operations manager is the leader of the team who takes care of the implementation concerning any specific department or process. They are chosen based on their technical knowledge and ability to coordinate people.
-
The Technical Experts Team
This is the team that is responsible for redesigning the inefficient processes. Anyone with sufficient technical knowledge can be the technical expert in the BPR team. The technical team members have to follow the plan put up by the senior management team and use their expertise to find and remove the inefficiencies in the process successfully.
Step 2: Measure Existing Processes and Spot Inefficiencies
An important step to take before implementing a new and completely different system in place, it is necessary to understand whether that new system is required or not. To find this out, measuring the efficiency of the existing process is a must step. Until then, it is not ideal to disturb the flow of the process.
Drawbacks within the processes can be measured by looking at the performance and the output that is generated. Match these outputs with the goals that were set before beginning the process. On a secondary level, the output can also be judged using the average industrial performance with similar processes. This will give a picture of the standard of performance in comparison to the competitors.
Once this is done, the root cause of all inefficiencies can be spotted and added to the list of improvements. Depending on the number of processes that require improvement, the organization can decide on the need for a business process reengineering.
Step 3: Communicate the Need for Change
Communicating the upcoming change to the workforce and the stakeholders is crucial. Not all changes are naturally accepted by everyone. Some may resist and will require time to understand the necessity of this change. Therefore, this needs to be properly communicated. The purpose, the changes that are expected to be made, and the expected goals have to be conveyed closely and accurately. A successful BPR strategy will bring more benefits by removing the challenges faced before.
Introducing strategies like automation can easily improve the quality of the work and also reduce the workload of the employees. They can invest their time and energy in high-value and meaningful tasks. This will maintain the motivation and morale of the employees as well. Here are some of the positive change management practices that can be followed:
- Communicate the vision clearly
- Acknowledge the essentiality of every employee
- Listen to the employees’ concerns
- Be ready to modify the change at any point
Step 4: Map out the Future Processes
Plan the future processes in terms of how you want them to look and work. Creating a new diagram that will give a simplified understanding of what the future processes will look like. This will ultimately help in determining new tools and software that can be implemented to streamline process workflows and cut down on the burden on your employees.
Step 5: Pick Relevant KPIs and Monitor Them Constantly
Setting the key performance indicators will give a framework to judge the performance of the newly introduced process reengineering. With predefined metrics, a better understanding of the new design is established and can be used to determine the success rate of the reengineering process. Some of the most common KPIs used by different departments are as follows:
Sales Department KPIs:
- Average deal size
- Closed deals per representative
- Customer loyalty
- Number of deals per partner
- Sales cycle time
Marketing Department KPIs:
- Ad click-through ratio
- Cost per lead
- ‘Effective reach
- Response rate
- Customer acquisition cost
Finance Department KPIs:
- Cost of Accounting
- Cost per transaction
- Time taken to process payroll
- Cost of goods sold
- Earnings before interest and taxes
Step 6: Implement the New Process
Once all the pre-reengineering setup has been completed, it is time to finally implement that change. As the need for change has been communicated, and the project requirements and KPIs are set, implementation can be carried out. The key point to follow is making small changes during the implementation process. As mentioned earlier, a sudden change in the complete process might not be ideal or successful.
Step 7: Compare KPI Performance and Evaluate the Project Success
Once the changes have been implemented, it is now the stage to check the performance of the process using the set KPIs. If the new process is found to be lacking, a complete analysis of the system can be performed again and identify the drawbacks. It is also essential to check whether the changes that have been made are not affecting the existing processes that were not processed in BPR. Therefore, the effects of the business reengineering process have to be checked in the overall working of the organization.
Real-Life Business Process Reengineering Examples
Here are some of the real-life Business Process Reengineering examples companies to learn from:
Ford Motor Company – Business Process Reengineering Examples
The automobile manufacturer Ford Motor Company, today well-known for its strong brand recognition and innovative products, was struggling to create a spot for itself in the industry in the 1990s among strong competitors like Toyota and Honda. This is where the company initiated a series of BPR activities that completely transformed the business to efficiency. Let us explore the case further.
Case Study 1:
The underlying problem was found to be the lack of management in the supply chain. Added to this, long lead times, extreme inventory expenses, and several supply chains, visibility was reduced drastically. With these many issues, the company was in a spot where it could not properly respond to the changes in customer demand and also had the power to mark itself in the market.
The Business Process Reengineering Initiative by Ford
The first initiative introduced by Ford Motor Company was to reengineer their supply process by introducing a new system called the Ford Production System (FPS). This system aimed to reduce lead times, enhance supplier performance and management, and also regulate the inventory costs that came in.
Implementing the change in the existing system provided the company with clarity and visibility into supplier management and also understanding the changing customer behavior and demand. Gradually, Ford was empowered to attain a new level of efficiency, elevate their customer satisfaction, and also increase their profit enabling them to create a spot for themselves in the industry.
Case Study 2:
In a different case, during the 1980s, several American companies were aiming to reduce the administrative and other expenses of the company, Ford was looking up ways to do this. That is when one of their competitors, Mazda, was running their accounts payable department with only 5 workers. Taking this into consideration, Ford figured their workforce could also be reduced to 100.
Ford decided to go with automation software that stored and transferred information automatically, reducing the number of employees needed for manual data entry. This innovative strategy completely changed the accounts payable process to much more efficiency. The reengineered process had the following workflow:
- The purchasing department initiates an order which is automatically updated on the online database.
- The resource handling department receives the goods and matches the order details with the product and the information on the database.
- If the order details match, the material control accepts the order on the system.
Airbnb – Business Process Reengineering Examples
Airbnb is one of the most popular online marketplaces that helps travelers connect with short-term and long-term homestays and people who lend spaces to rent.
The Issue
The system in place with Airbnb was filled with bottlenecks and hence delays were often caused, pulling down the efficiency of the process. Since the business had to connect several factors to make the process run, there were delays in the payments made and the process remained complicated and chaotic. As the effects of the lack of a basic management system, Airbnb had to face several obstacles with the booking process, where they had to manually enter data, zero standardization, and delays in the responses received.
The Business Process Reengineering Initiative by Airbnb
The challenges were tackled by introducing a new automated booking system. Using automation, the manual data entry was transformed and standardization was brought into the process. Streamlining and optimizing certain inefficient tasks completely changed how processes were carried out. Implementing these changes enabled Airbnb to enhance its processes and operations and maintain a consistent rate of customer satisfaction and revenue generation.
Honeywell – Business Process Reengineering Examples
Honeywell is an engineering and technology company that manufactures products for aerospace and automotive products, and control systems for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes. It specializes in chemicals, plastics, and engineered materials.
The Issue
In the 1990s, with many defects and issues in one of their industrial automation and control business units, Honeywell decided to go in for the business process reengineering process. Managing the defects and reducing the cycle time were the two most important key performance indicators set by the company. Their BPR strategy was initiated by analyzing and detecting the problems within the production process. The primary issues were found to be the following:
- The most probable cause of note when teams failed was due to the inefficiency of the authority to make decisions.
- It was found that each team was only taking care of the quality control of their respective teams and there was coordination between the teams to ensure the quality control as well.
The Business Process Reengineering Initiative by Honeywell
The lack of teamwork and proper coordination were the core problems, so the company decided to go with BPR. Their strategy was to analyze and map the processes and how to effectively communicate inefficiencies to the workforce. The most crucial thing they did was to completely stop the production for some time.
Following this, the employees were made to take an extensive training session that helped them understand the new production system. Additionally, to elevate the workers’ sense of responsibility, teamwork, and morale, the company scrapped fixed wages and implemented a salary-based compensation that will be determined by the performance levels of the individual workers.
Along with this, quality management, and the TotalPlant factory program were introduced. The old system of integrated hardware, and software programs was removed. Through this reengineering process, Honeywell was able to reduce the following:
- Defects rates by 70 percent
- Customer rejections by 57 percent
- Cycle time by 72 percent
- Inventory investment by 46 percent
- Customer lead times by over 70 percent
Conclusion on Business Process Reengineering Examples
From the business process reengineering examples of Ford, Airbnb, and Honeywell, we can deduce that BPR is a robust strategy to undertake. Solutions like automation, business process improvement, providing training sessions, etc. are efficient BPR strategies that organizations can implement if they are looking to improve efficiency.
Tips for Business Process Reengineering
To acquire a successful implementation, there are a few tips that can be followed by organizations. These tips can guide firms to fix a framework to follow and make result-oriented decisions. Here are a few tips:
1. Identify the Goals and Purpose
The most important thing to do is to have an idea about the goals of your organization, and it is extremely important to determine the purpose of the process as well. When the goals are fixed, the processes can be effectively judged. If the processes are found to be inefficient, then organizations will be in a position to determine whether they require a BPR strategy to be implemented. In this scenario, with the goals in mind, the organizations will be able to clearly define the purpose of the reengineering as well.
2. Consider the Tools
Leveraging a solid tool is highly recommended as one of the best ways to carry out the process. These software tools can be upgraded according to the organization’s needs. Even upgrading the equipment regularly makes it easier for the employees to work more efficiently, and securely.
3. Look to the Future
Keeping up with the trends is essential to keep pace with the fast-moving technological updates. This also aids in meeting the changing demands of the clients as well.
Business Process Reengineering Tools
Introducing a complete revamp of the process is a tedious and hectic task. Making a significantly bigger change in the existing workflows can be challenging in many ways. Tackling these challenges can be made easy with the help of business process reengineering tools. These tools have the potential to detect, analyze, and erase the inefficiency in the processes through operations like automation, collaboration, etc. Let us look into some of the most influential BPR tools.
1. Cflow
Cflow is a powerful workflow automation tool that can drastically transform the performance of business operations. Being a no-code workflow platform, it is user-friendly and a perfect solution for improving business processes to efficiency. Cflow allows its users to shift their focus to taking a more strategic and systematic approach to business process reengineering.
Why use Cflow?
Cflow’s workflow automation platform enables the following:
- The platform aids in creating flowchart-based workflows with just a drag-and-drop action. This feature comes along with in-built templates for all of the business processes.
- The tools let its users route tasks easily. Users can also generate customized reminders and notifications regarding tasks, deadlines, and approvals for the respective task.
- It allows you to achieve integration with several other third-party applications.
- It helps you receive customized visually appealing reports and analytics to assess the performance of both the tasks and the employees in the organization.
- The platform creates a secure place allowing one to have deeper insights and help make report-oriented decisions.
2. ProcessMaker
ProcessMaker is a visual workflow builder that optimizes several business processes. As a cloud-based software, the platform can automate operations and effectively manage all tasks. With its visual workflow editor, ProcessMaker enables users to create, manage, and monitor all the process workflows without the use of any code.
Why use ProcessMaker?
- As a visual workflow editor, the platform provides its users with drag-and-drop functionality to easily generate and manage workflows.
- The platform also gives readily available workflow templates that are customizable, making it easier for the users to initiate the process.
- The tool performs measured management of the tasks. It allows the easy assigning, delegation, and monitoring of the process in one space.
- It upholds a system of instant analytics and reporting on the performance of the different tasks.
3. Bizagi
Bizagi is an all-encompassing BPM suite that aids in creating, automating, and analyzing the performance of business processes. Like most of the BPR tools, Bizagi also offers a business process improvement system that uses a no-code visual workflow editor to enable users to create, manage, and track workflows effectively.
Why use Bizagi?
- The platform offers easy navigation with its drag-and-drop interface in the visual workflow editor.
- The in-built workflow templates are customizable helping teams reduce the time taken to create workflows for different common processes. The teams can make necessary edits to the workflow whenever necessary.
- The tool is cost-effective, scalable, and time-saving, and potentially enhances the process’s performance through effective streamlining.
Conclusion
From the different business process reengineering examples discussed here, we can understand that implementing business process reengineering is a good solution for every business.
However, if your business is falling behind in satisfying the changing trends and customer demands, it is always ideal to go for a business process reengineering process.
BPR may seem complex, but it can guide businesses to be in harmony with demand and trends and also reach the peak of efficiency and productivity.
Cflow is one of the best platforms for achieving successful business process reengineering without much confusion. To explore more about Cflow, sign up now!




