Understanding IT Framework: Types, Importance, and Best Practices

Key takeaways
- An IT framework provides a structured set of guidelines, processes, and best practices to manage and govern technology.
- Businesses use IT frameworks to align IT goals with organizational objectives, ensuring efficiency, compliance, and security.
- Popular IT frameworks include ITIL, COBIT, TOGAF, and NIST, each catering to specific governance and service needs.
- Implementing an IT framework helps in risk management, resource optimization, and digital transformation.
- Organizations adopting IT frameworks often achieve stronger compliance, better decision-making, and improved IT service delivery.
What is an IT Framework?
An IT framework is a structured set of rules, processes, and best practices designed to help organizations manage their information technology systems effectively. It acts as a roadmap that guides how IT resources, services, and governance should be handled to meet business goals. Organizations are provided with a structured framework for utilizing technology with an IT framework. This is where frameworks help, they ensure that IT operations are aligned with strategic objectives, security protocols, and compliance requirements.
The importance of an IT framework lies in its ability to create consistency, improve decision-making, and minimize risks. Instead of ad-hoc approaches, businesses can adopt well-established frameworks that bring clarity to IT service management, governance, compliance, and risk mitigation. In this blog, we will explore what an IT framework is, its types, examples, benefits, and why businesses should adopt them as part of their technology strategy.
Table of Contents
What is an IT Framework in Simple Terms
In the simplest terms, an IT framework is a structured set of practices, guidelines, and processes that help organizations manage how technology is used, maintained, and improved. Think of it as a rulebook that ensures every aspect of information technology, from hardware to software, data security to service delivery, works in harmony with business objectives. Instead of leaving IT operations to guesswork, frameworks provide a clear and consistent approach.
For example, just as an architect relies on blueprints to design a building, businesses rely on IT frameworks to design, govern, and operate their technology infrastructure. These frameworks ensure that IT resources are not only managed effectively but are also aligned with business strategies, security policies, and regulatory requirements.
An IT framework is not a one-size-fits-all solution, it is adaptable. Organizations can choose and tailor frameworks based on their industry, size, and compliance obligations. A healthcare provider might adopt a security-focused framework like NIST, while a financial institution may lean on COBIT for governance and risk management. This flexibility allows businesses to implement best practices without being locked into rigid models.
Most importantly, IT frameworks simplify complex IT operations. They break down large, complicated systems into manageable components such as governance, compliance, service management, and cybersecurity. This makes it easier for IT teams and business leaders to communicate, plan, and execute strategies effectively.
In short, an IT framework is a roadmap that ensures technology not only supports but also strengthens business performance, reduces risks, and promotes continuous improvement.
Difference Between IT Framework And IT Standard
Although the terms IT framework and IT standard are often used interchangeably, they serve different purposes within an organization’s technology ecosystem. Understanding this difference is crucial for businesses looking to balance flexibility with compliance.
An IT framework provides a structured set of best practices, principles, and guidelines that help organizations align their IT operations with business goals. Frameworks are adaptable, meaning they can be customized to fit the specific needs of a company or industry. For example, ITIL offers practices for IT service management, but organizations can apply only the modules relevant to their operations.
An IT standard, on the other hand, is a formalized and mandatory set of rules or specifications established by authoritative bodies. Standards leave little room for flexibility and must be followed strictly, especially in industries where regulatory compliance is non-negotiable. For instance, ISO 27001 sets exact requirements for managing information security, and businesses must comply fully if they want to achieve certification.
To better understand how the two differ, let’s look at a structured comparison:
Aspect | IT Framework | IT Standard |
Definition | A set of best practices and guidelines for managing IT processes and resources | A formal set of requirements, rules, or specifications for IT operations |
Flexibility | Highly flexible, can be tailored to business needs | Rigid, compliance is mandatory |
Purpose | Provides direction, improves IT governance, and enhances efficiency | Ensures compliance, uniformity, and adherence to regulations |
Examples | ITIL, COBIT, TOGAF, NIST Cybersecurity Framework | ISO 27001, PCI-DSS, GDPR |
Adoption | Voluntary, chosen based on organizational needs | Mandatory, especially for regulatory or industry requirements |
In practice, most organizations use a combination of both. Frameworks offer guidance and adaptability to improve IT service delivery and governance, while standards enforce uniformity and legal compliance. For example, a company may use ITIL for managing IT services while also adhering to ISO 27001 to ensure its data security practices meet international standards.
By striking the right balance between frameworks and standards, organizations can remain agile while still ensuring compliance with industry regulations and customer expectations.
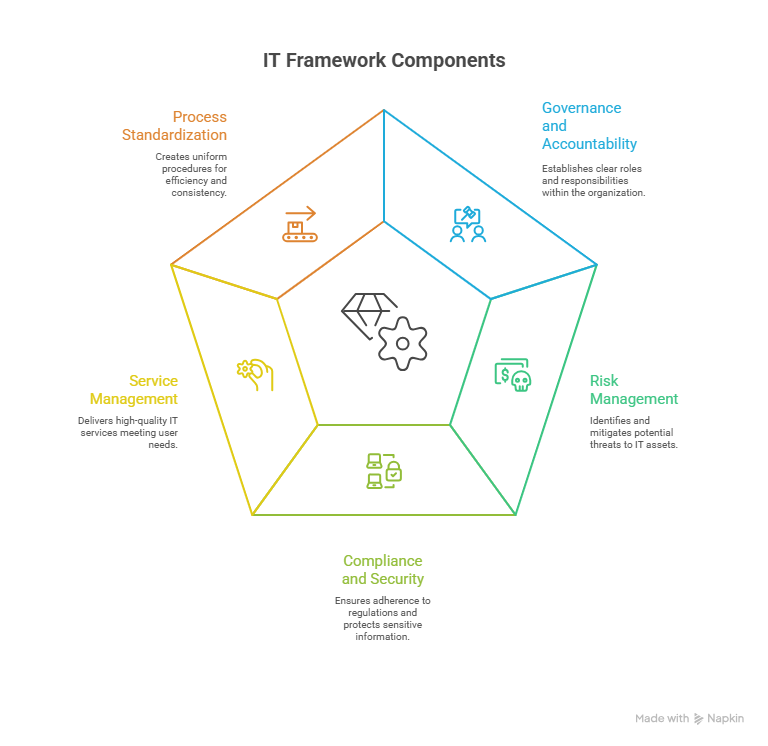
Key Components Of An IT Framework
Every IT framework is built on a set of essential components that ensure technology is managed effectively, securely, and in alignment with business objectives. While the specific focus may differ across frameworks, most share a few core elements that define how IT should be structured and governed. Understanding these components helps organizations see the bigger picture of why frameworks are necessary.
Governance And Accountability
Governance is the backbone of any IT framework. It defines the roles, responsibilities, and decision-making structures for IT within an organization. This ensures that accountability is established and IT initiatives are always tied to business goals.
Example: COBIT emphasizes governance by clearly defining decision rights and ensuring accountability for IT resources and outcomes.
Risk Management
Managing risks is a critical component of IT frameworks. Risk management involves identifying potential threats, such as data breaches, downtime, or compliance violations, and putting measures in place to mitigate them.
Example: The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides a structured approach for assessing and reducing cybersecurity risks, helping businesses safeguard critical data.
Compliance And Security
Most IT frameworks emphasize compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements. They provide structures to ensure IT practices meet legal obligations while protecting sensitive data.
Example: ISO/IEC 27001 focuses on building strong security policies and controls to protect organizations from data leaks and compliance failures.
Service Management
IT frameworks often include guidelines for how IT services should be delivered, monitored, and improved. This component ensures that IT functions reliably and meets the needs of end-users.
Example: ITIL defines best practices for service delivery, including incident management, service continuity, and customer support, making IT more responsive and efficient.
Process Standardization
Standardizing IT processes ensures consistency across teams and departments. Frameworks outline workflows, documentation, and performance metrics so that organizations can streamline operations and avoid duplication of effort.
Example: CMMI promotes process maturity by encouraging organizations to document, standardize, and continuously improve IT processes.
Performance Monitoring And Continuous Improvement
A vital part of IT frameworks is the focus on measuring performance and seeking ongoing improvements. By tracking KPIs and conducting regular audits, organizations can refine their IT strategies and remain adaptable in changing business environments.
Example: TOGAF encourages continuous improvement of IT architecture to ensure long-term scalability and efficiency in enterprise systems.
Types Of IT Frameworks
There are several types of IT frameworks, each created to address specific needs such as service management, governance, architecture, security, or operations. No single framework fits all organizations, businesses often adopt one or more based on their goals, industry, and compliance requirements. Below are some of the most widely used IT frameworks along with practical examples of how they are applied in real-world scenarios:
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
ITIL is one of the most recognized IT service management frameworks. It provides structured practices for delivering high-quality IT services while ensuring alignment with business needs. The framework emphasizes processes such as incident management, problem management, and service delivery.
Example: A global IT services company uses ITIL to handle customer support more efficiently. By following ITIL’s incident management practices, the company can resolve issues faster, improving client satisfaction and reducing downtime.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology)
COBIT focuses on IT governance, compliance, and risk management. It helps organizations ensure that their IT resources are used responsibly and that risks are managed effectively. COBIT is especially relevant in regulated industries such as banking and finance.
Example: A financial institution implements COBIT to strengthen its IT governance and ensure compliance with regulations like SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act). By doing so, the bank reduces risks of fraud and ensures accountability in IT operations.
TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework)
TOGAF is widely used for enterprise architecture. It helps organizations design, plan, implement, and manage IT infrastructure in a structured way. TOGAF supports large-scale digital transformation by aligning IT systems with business strategies.
Example: A multinational manufacturing company uses TOGAF while upgrading its legacy systems. By applying TOGAF’s methodology, it creates a unified IT architecture that supports global operations and reduces integration challenges.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework provides guidelines for managing and reducing cybersecurity risks. It is often adopted by organizations that prioritize data security and compliance with regulations.
Example: A healthcare provider adopts the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to safeguard patient records and comply with HIPAA regulations. This ensures that sensitive health data is protected from cyberattacks while maintaining patient trust.
DevOps Framework
Unlike traditional frameworks, DevOps is more of a cultural and operational approach that emphasizes collaboration between development and IT operations teams. Its focus is on automation, continuous integration, and rapid software delivery.
Example: A SaaS startup uses DevOps practices to release updates weekly instead of quarterly. Automation tools enable the company to test and deploy software faster, enhancing user experience and staying ahead of competitors.
ISO/IEC 27001
While technically a standard, ISO 27001 is often used alongside IT frameworks as part of information security management. It defines strict requirements for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Example: An e-commerce company adopts ISO 27001 to protect customer payment information. Achieving certification helps the company build trust with customers while ensuring compliance with international security requirements.
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration)
CMMI is a process improvement framework that helps organizations enhance their software development and IT management maturity. It evaluates processes across multiple levels to identify strengths and weaknesses.
Example: A government IT contractor uses CMMI to improve software development quality. By progressing to a higher maturity level, the contractor ensures consistent project delivery and strengthens its credibility for future contracts.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
Benefits of Using an IT Framework
Adopting an IT framework is not just about standardizing processes, it directly impacts business performance, governance, and long-term growth. Frameworks provide the structure organizations need to manage IT effectively, reduce risks, and align technology with strategic objectives. Below are the major benefits of implementing an IT framework, along with practical insights:
Alignment With Business Goals
One of the biggest advantages of IT frameworks is their ability to align IT operations with overall business objectives. Instead of IT functioning in isolation, frameworks ensure that every technology decision supports broader business priorities such as growth, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Example: An e-commerce company adopts ITIL to improve service management, ensuring IT services directly support sales and customer experience strategies.
Improved Compliance And Regulatory Adherence
Many industries, such as finance and healthcare, are heavily regulated. IT frameworks provide structured processes to ensure that organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards without ambiguity. This minimizes risks of non-compliance, which can lead to penalties and reputational damage.
Example: A healthcare provider uses the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to comply with HIPAA regulations and ensure the protection of patient records.
Stronger Risk Management
IT frameworks help organizations identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks systematically. From cybersecurity threats to operational inefficiencies, frameworks provide structured approaches to reducing vulnerabilities and ensuring resilience.
Example: A financial services company adopts COBIT to manage IT governance and minimize risks related to fraud, data breaches, and system failures.
Efficiency In IT Operations
Standardized processes reduce redundancies, eliminate confusion, and streamline workflows. This results in improved productivity for IT teams, quicker resolution of issues, and smoother service delivery across the organization.
Example: A telecom company implements ITIL practices for incident management, cutting average resolution time by 40% and ensuring uninterrupted service for its customers.
Better Decision-Making
IT frameworks establish clear accountability, performance metrics, and reporting structures. This transparency enables leadership teams to make data-driven decisions with confidence, improving both strategic planning and day-to-day operations.
Example: A manufacturing enterprise uses TOGAF to design its IT architecture, enabling leaders to make more informed decisions about resource allocation and technology investments.
Support For Digital Transformation
Organizations undergoing digital transformation benefit greatly from IT frameworks, as these frameworks provide the structure needed to adopt new technologies while minimizing disruption. They ensure that cloud adoption, automation, and AI integration are implemented systematically.
Example: A logistics company applies TOGAF while moving to cloud-based systems, ensuring that the new IT architecture supports scalability and future innovation.
Enhanced Customer And Employee Experience
Well-structured IT operations not only improve backend processes but also directly influence customer satisfaction and employee productivity. By reducing downtime, improving security, and ensuring seamless service delivery, frameworks help organizations build trust and loyalty.
Example: A global IT service provider uses ITIL to deliver faster, more reliable support services, resulting in improved client satisfaction scores.
Examples Of IT Frameworks For Businesses
Organizations across industries rely on IT frameworks to strengthen governance, compliance, and efficiency. For instance, banks and financial institutions often adopt COBIT to manage compliance and risk. Healthcare providers use NIST frameworks to safeguard patient data. IT service companies implement ITIL for smooth service delivery. Enterprises undergoing large-scale digital transformation may turn to TOGAF for structured IT architecture.
Each framework has unique strengths, and many organizations adopt a combination of frameworks to meet their specific requirements.
Where Does Cflow Fit Into Your IT Framework
Cflow is not an IT framework by itself, but it is a powerful enabler that helps organizations implement and execute frameworks more effectively. Most IT frameworks provide guidelines and best practices, but businesses often struggle with execution due to manual processes, siloed tools, and lack of visibility. This is where Cflow adds value by automating workflows, ensuring compliance, and streamlining IT service delivery.
With its no-code, AI-powered automation capabilities, Cflow aligns seamlessly with the core components of leading IT frameworks like ITIL, COBIT, and NIST. By digitizing repetitive processes, ensuring data security, and providing real-time insights, Cflow transforms frameworks from theoretical models into practical, functioning systems.
Here’s how Cflow supports your IT framework implementation:
- Governance And Accountability: Cflow automates approvals, routing, and reporting, ensuring clear accountability across IT operations while reducing delays and errors.
- Risk And Compliance Management: Built-in rules, audit trails, and data security features make it easier to comply with industry standards and reduce risks of non-compliance.
- Service Management: From incident tracking to change requests, Cflow simplifies IT service workflows, enabling faster response times and better user satisfaction.
- Process Standardization: Cflow enforces consistency by standardizing IT workflows across teams, departments, and regions, ensuring uniformity with your chosen framework.
- Performance Monitoring: Real-time dashboards and analytics provide visibility into KPIs, allowing leadership to track progress and continuously improve IT operations.
In essence, while frameworks provide the “what” and “why,” Cflow delivers the “how.” It bridges the gap between guidelines and execution, helping organizations gain the true benefits of IT frameworks by making processes practical, scalable, and efficient.
Importance Of IT Frameworks For Modern Organizations
As businesses increasingly depend on digital systems, the role of IT frameworks becomes critical. Without them, IT functions can become fragmented, leading to inefficiency, security gaps, and compliance issues. Frameworks bring uniformity across processes, ensure accountability, and provide a foundation for scalability.
They are also vital in industries with stringent regulatory requirements such as healthcare, finance, and government. By adopting the right IT framework, organizations can build resilience, improve operational agility, and gain a competitive advantage.
Final Thoughts
An IT framework is more than just a set of guidelines, it is a foundation that ensures IT systems align with business objectives, remain secure, and operate efficiently. From ITIL to NIST, these frameworks provide organizations with a structured way of managing technology while adapting to evolving digital needs.
Cflow, an AI-powered workflow automation platform, can help organizations implement IT frameworks effectively by streamlining processes, automating compliance, and providing real-time visibility into IT operations. By combining automation with proven IT frameworks, businesses can achieve stronger governance and better results. Start leveraging Cflow to bring structure and efficiency to your IT framework adoption journey.
FAQs
1. What is an IT framework?
An IT framework is a structured guideline that defines how organizations should manage their IT resources, governance, and services to align with business goals.
2. Why do businesses need an IT framework?
Businesses need IT frameworks to ensure consistency, compliance, risk management, and efficiency in IT operations.
3. Which IT frameworks are most commonly used?
The most common IT frameworks include ITIL for service management, COBIT for governance, TOGAF for architecture, and NIST for cybersecurity.
4. What is the difference between IT frameworks and standards?
Frameworks are flexible guidelines that organizations adapt, while standards are mandatory and enforce strict compliance.
5. Can small businesses use IT frameworks?
Yes, IT frameworks are scalable and can be adapted to fit the size and needs of small businesses as well as large enterprises.
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business:

Do better workflow automation with Cflow
Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms, etc. to save time and cost.

Talk to a workflow expert
Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize your daily tasks.

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master workflow automation.