Automated Data Processing: Unlocking Speed, Accuracy, and Scalability for Modern Workflows

Key takeaways
- Automated data processing streamlines how data is collected, organized, and analyzed without manual intervention.
- Businesses benefit from real-time data access, better decision-making, and scalable workflows.
- Automation tools reduce human error, accelerate data flow, and improve data governance.
- Intelligent data processing enables use cases in sales, marketing, finance, and operations.
- This blog covers what automated data processing is, its benefits, tools, examples, and implementation strategies.
Table of Contents
What Is Automated Data Processing?
Automated data processing is the use of technology to capture, organize, clean, analyze, and store data with little to no human intervention. It replaces manual tasks such as data entry, sorting, report generation, or system updates with automated workflows that run continuously or on trigger-based logic.
For example, instead of manually exporting a CSV file, cleaning the data in Excel, uploading it into a CRM, and then creating a report, automated data processing tools can perform these tasks behind the scenes—triggered by an event, like a form submission or file upload. The processed data can be pushed directly into analytics dashboards, cloud storage, or downstream systems in real-time.
This automation is powered by a combination of rule-based logic, APIs, and increasingly, machine learning algorithms that enable the system to detect patterns, flag anomalies, and adapt over time. The Automated Data Processing Market is projected to grow from USD 635.59 billion in 2025 to reach USD 1306.14 billion by 2034.
Why Should You Automate Data Processing?
Data is everywhere—from customer interactions and financial transactions to marketing campaigns and inventory systems. But collecting data is only half the equation. For it to drive meaningful action, it must be processed, structured, analyzed, and delivered—fast and accurately. Manual methods simply can’t keep up with today’s data velocity and volume.
That’s where automated data processing comes in. It refers to the use of software systems and workflows to automatically transform raw data into usable insights, often in real-time. In this blog, we’ll explore what automated data processing is, its real-world applications, the benefits of using it across business functions, and how to implement it using intelligent, no-code platforms.
Manual data handling is not only time-consuming—it’s error-prone, inefficient, and unsustainable at scale. As businesses grow and interact with more platforms and customers, the volume of data they generate multiplies exponentially. Automating data processing becomes not just a convenience but a strategic imperative.
One of the primary reasons to automate is data consistency. When teams manually input or transfer data between systems—say, from web forms to a CRM or from sales dashboards to spreadsheets—discrepancies creep in. Even minor errors in customer information, lead scoring, or segmentation criteria can cause downstream confusion, misreporting, or lost revenue opportunities.
Automation ensures data accuracy at every touchpoint, providing a unified and real-time view of customer interactions, marketing performance, and sales conversions. In turn, this improves personalization, lead qualification, and campaign effectiveness.
Another compelling reason is speed-to-action. Modern buyers expect fast, tailored responses. If your system processes data only once a day or relies on someone to update records manually, you risk missing out on timely engagement. With automation, data updates happen instantly—triggering follow-ups, campaigns, or alerts based on user behavior the moment it occurs.
In addition, automation enhances compliance and security. It minimizes the need to manually transfer sensitive data, reducing exposure to leaks or mismanagement. Audit trails, encryption, and system logs ensure accountability and support regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Ultimately, automating data processing frees up your team to focus on value-added work—strategy, analytics, and customer relationships—rather than wasting hours on repetitive admin tasks. Whether you’re running a lean startup or scaling an enterprise, automation is the key to making data a real-time business asset instead of a bottleneck.
Components of Automated Data Processing
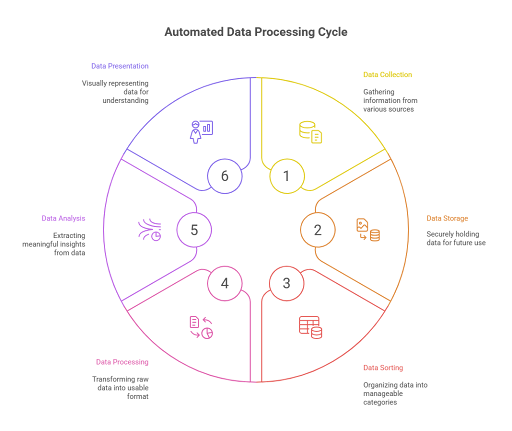
Automated data processing isn’t a single action—it’s a system made up of interconnected components that work together to transform raw inputs into actionable intelligence. Understanding these core components helps businesses design efficient, scalable, and secure data workflows.
1. Data Ingestion
The first step is collecting data from multiple sources. This can include web forms, APIs, IoT devices, CRM systems, spreadsheets, or external databases. Automated ingestion ensures data is pulled in consistently and without delay, eliminating the need for manual data entry or file uploads.
2. Data Transformation and Cleaning
Once collected, raw data often needs to be standardized, validated, or reformatted. This includes removing duplicates, correcting errors, converting file types, or applying business rules. Automation ensures this transformation happens instantly and according to predefined logic—improving the quality and consistency of your dataset.
3. Workflow Rules and Trigger Logic
At the heart of automated data processing are rules that dictate how data moves through the system. These rules include triggers (e.g., “when a form is submitted”), conditions (e.g., “if industry = software”), and actions (e.g., “send to sales CRM”). This component is where business logic is embedded, ensuring that each piece of data goes exactly where it needs to, when it needs to.
4. Data Storage and Integration
Processed data needs to be stored in secure, centralized systems—whether that’s a data warehouse, cloud storage, or a business intelligence tool. This component also includes integration with downstream systems like ERPs, CRMs, marketing platforms, or analytics dashboards to ensure seamless data flow across your tech stack.
5. Analytics and Reporting
Automated systems don’t just store data—they prepare it for analysis. Once structured and enriched, the data can be fed into dashboards or reports automatically, allowing teams to monitor KPIs, detect anomalies, and make informed decisions without waiting for manual report generation.
6. Monitoring and Error Handling
No system is perfect, so monitoring is critical. This component includes error alerts, logging, retry mechanisms, and validations that ensure the data pipeline operates smoothly. Any failures in data delivery or transformation are flagged and handled automatically, reducing downtime and preventing data loss.
7. Security and Compliance Controls
Data privacy and integrity are built into the automation stack through access controls, audit trails, encryption, and policy enforcement. This ensures that sensitive data is protected and that processing activities comply with relevant laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.
Benefits of Automated Data Processing in Business Workflows
Automating data processing brings both operational and strategic benefits. Here’s how businesses gain by adopting automated systems. A 2021 report reveals that 90% of knowledge workers confirm automation has improved people’s lives in the workplace.
Increased Speed and Real-Time Availability
Manual data handling is slow and often subject to batch processing. Automated workflows, on the other hand, run in real-time or near-real-time. This means decision-makers can act on current data rather than outdated reports. Whether you’re syncing customer data or updating inventory, speed becomes a competitive advantage.
Higher Accuracy and Reduced Human Error
Data entry errors, duplication, and missed updates are common in manual processes. Automation eliminates these inconsistencies by standardizing how data is collected, validated, and shared across systems. This improves the overall data quality and builds trust in your analytics.
Scalable Data Operations
As your business grows, so does the volume and complexity of your data. Automated data processing systems scale effortlessly—handling thousands or millions of records without needing additional resources or staff. This is especially useful in data-heavy functions like e-commerce, finance, or SaaS operations.
Improved Data Governance and Compliance
Automation tools often include built-in controls for tracking data sources, logging changes, and enforcing access permissions. These features support better compliance with data regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA and provide audit trails for accountability.
Cost Savings Over Time
Though automation may require initial setup, it reduces long-term operational costs. Businesses save on labor, reduce data-related errors, and free up skilled teams to focus on analysis, strategy, and innovation instead of manual upkeep.
Real-Time Automated Data Processing vs. Batch Processing
When it comes to automating data workflows, businesses typically choose between two fundamental processing modes: real-time processing and batch processing. Both serve different purposes and have their place depending on the context, volume, and urgency of data.
Real-time automated data processing involves processing data immediately as it becomes available. It’s triggered by events or inputs—such as a customer submitting a form, making a purchase, or interacting with a website. In these scenarios, the system collects, transforms, and routes the data within seconds. Real-time processing is especially crucial for applications that require immediate responses, like fraud detection, personalized recommendations, or lead capture and assignment.
Batch processing, on the other hand, involves collecting and storing data over a period of time and then processing it all at once. This method is ideal for high-volume tasks that don’t require instant action, such as payroll, end-of-day reports, or monthly inventory audits. While not instantaneous, batch processing is efficient for handling large datasets with fewer resource demands per cycle.
The choice between real-time and batch processing depends on the business’s goals, data sensitivity, and the need for speed versus scale.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison:
Comparison: Real-Time vs. Batch Data Processing
Feature | Real-Time Automated Data Processing | Batch Data Processing |
Processing Frequency | Continuous or event-triggered | Scheduled (e.g., hourly, daily, monthly) |
Latency | Near-instant (seconds to milliseconds) | High (minutes to hours) |
Best For | Time-sensitive tasks (e.g., alerts, personalization) | High-volume, non-urgent tasks (e.g., reporting) |
Typical Use Cases | Fraud detection, lead routing, live dashboards | Payroll, data backups, bulk data uploads |
System Requirements | Requires constant availability and monitoring | Can run during off-peak hours with fewer resources |
Data Volume Handling | Efficient with small, continuous inputs | Efficient with large, aggregated datasets |
Complexity | Higher due to event-driven architecture | Simpler to design and monitor |
User Expectations | Supports real-time customer experiences | Supports internal processes and analytics |
Error Handling | Needs real-time validation and recovery workflows | Errors can be caught and corrected in batches |
Examples | Chatbot input processing, IoT alerts | Quarterly sales analysis, compliance reporting |
Both methods can coexist within a single organization. For instance, a company might use real-time processing to track user behavior on a website and trigger email campaigns, while using batch processing to generate weekly financial reports. The key is to align the processing method with the business context, data criticality, and system infrastructure.
Examples of Automated Data Processing in Action
To illustrate how this works, let’s look at real-world scenarios across different departments:
Marketing Automation
When a new lead downloads a whitepaper, an automation tool can capture their data, enrich it with location and firmographic information, push it into the CRM, and assign a lead score. This removes the need for manual entry and enables timely follow-up.
Sales Operations
Sales teams use automated data processing to sync CRM updates with email activity, calendar invites, and proposal systems. All this happens behind the scenes, ensuring the pipeline is up-to-date without sales reps having to log every interaction.
Finance and Accounting
Invoices scanned via OCR are automatically matched with purchase orders, checked for duplicates, and routed for approval. This streamlines accounts payable and reduces the risk of payment errors or delays.
Customer Support
Support tickets submitted via email or chat can be tagged, categorized, and routed to the correct team automatically. Key customer data is extracted and stored, making it easier to generate support analytics or customer health scores.
Inventory Management
When a product stock drops below a threshold, the system automatically pulls reorder data, updates internal systems, and notifies suppliers. This just-in-time response prevents stockouts and improves procurement efficiency.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
Role of Procurement Compliance in Public Sector Purchasing
In the public sector, procurement compliance is non-negotiable. Taxpayer money is at stake, and transparency is mandatory. Every step—from tendering to vendor selection to payment—must be documented, justified, and publicly defensible.
Public sector entities face strict regulations around competitive bidding, conflict of interest disclosures, and contract limits. Digital procurement systems ensure these rules are enforced consistently.
Automated audit trails, pre-approved vendor lists, and budget validation workflows help reduce risk while maintaining public trust. With tools like Cflow, public sector organizations can meet both operational needs and legal obligations without compromising either.
Final Thoughts
Procurement compliance is no longer optional—it’s foundational to building a responsible, transparent, and resilient procurement function. Organizations that invest in compliance systems not only reduce risk and improve efficiency but also gain a competitive advantage through better supplier relationships and stronger financial control.
Cflow makes procurement compliance easy to implement and manage. With customizable, no-code workflows, automated approvals, real-time visibility, and audit-ready documentation, Cflow supports procurement teams in maintaining integrity, speed, and control—every step of the way.
Ready to automate your procurement compliance? Get started with Cflow and make compliance a built-in advantage, not a burden.
FAQs
What is procurement compliance?
Procurement compliance refers to following internal policies and external regulations in purchasing processes, including approvals, vendor selection, and contract execution.
How can automation help with procurement compliance?
Automation ensures that every purchase request follows predefined rules, routes to the correct approvers, and is documented for future audits—reducing errors and improving efficiency.
What makes Cflow a good solution for procurement compliance?
Cflow offers no-code workflow automation, multi-level approval routing, integration with finance tools, and audit-ready logs—making it ideal for organizations that want visibility and control over every purchase.
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business:

Do better workflow automation with Cflow
Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms, etc. to save time and cost.

Talk to a workflow expert
Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize your daily tasks.

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master workflow automation.