Business Activity Monitor (BAM): An Overview

What is Business Activity Monitor (BAM)?
Business activity monitoring (BAM) is the real-time monitoring of an organization’s business processes. It is a method used to identify bottlenecks, non-standard activities, and inefficiencies in an organization’s business process.
In addition, it helps to identify the causes of problems and their impact on ongoing business activities. Business activity monitoring supports operational decisions and ensures adherence to legal requirements, service level agreements (SLAs), and corporate policies by providing valuable information about daily business operations.
BAM can be used for both internal and external processes by combining data analysis and process interpretation to determine how well the business is performing or where it needs improvements.
This can also be done by analyzing data from different sources, including ERP systems, CRM systems, ERP logs, and other processes. BAM also provides some advanced features like SAP BW integration and BI tool integration which make it possible for you to develop custom dashboards based on your requirements.
Need for Business Activity Monitor
Business Activity Monitor (BAM) is a powerful and efficient tool that helps businesses improve their processes in many ways. It helps them to improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, increase employee productivity, and improve customer loyalty.
The following are some of the benefits that you can get from using BAM:
Customer satisfaction
- BAM gives you an insight into how your customers feel about your business and its products/services.
- This information will help you decide whether there are any areas where further improvements can be made to make them more satisfied with what they buy from your company.
Cost savings
- By monitoring operational activities such as inventory levels or product usage patterns, it becomes easier for managers at any level to identify which processes need improvement or optimization.
- You can save time and resources by implementing new ones without first checking if those improvements will result in cost savings over time.
Real-Time Process Analytics Using BAM
Real-time process analytics refers to processing data for automation, process optimization, and management. Business activity monitor aims to measure your business process activities with minimal delay possibly in real-time. It records all your process-related data and transforms it into ratios which are then used to measure the KPI targets. These KPI targets are defined by your business and with BAM, managers can become aware of the exceptions. These exceptions can either be opportunities or problems. Due to the nature of the BAM, managers can react to these exceptions proactively as they can use real-time information.
For instance, Cflow’s BAM can be used to observe all your process-relevant activities that happen across your organization. You can integrate activity information and commute metrics and implement business rules to set thresholds for easy visualization of the monitored data.
Business activity monitoring goes beyond just monitoring KPIs. It can also capture static KPIs, and filter and transform event-based process analytics in real time. Moreover, BAM systems necessarily don’t need to be passive and restricted to just observing and executing processes. They can also be set to notify managers of critical situations and automatically trigger escalation activities.
Elements of Business Activity Monitor
Business Activity Monitor (BAM) will help managers and executive teams understand their business units’ performance. It consists of multiple elements that constitute a monitoring system.
Business process measurement:
Business Process Measurement (BPM) is a way to monitor and measure business processes, which can be used for:
- Measuring the performance of a process or process improvement.
- Automating business processes.
Item instance monitoring:
An item instance is a business object that has been instantiated in your system. It represents the smallest unit of business process monitoring, which can be used to monitor individual instances of an item by using its unique identifier (ID).
Metric:
A metric is a value that is calculated from data. It’s an aggregation of data points and can be used to measure the performance of a business process. A metric is often expressed as an objective or goal, such as sales revenue per employee or customer satisfaction rate.
KPIs:
KPIs are key performance indicators. They measure the performance of a business process and help you identify where your organization needs improvement. KPIs can be used to monitor every aspect of your business, from sales through customer service to operations efficiency.
KPIs are especially useful for businesses that need more than one data point for their processes. If there were only one metric for each process, it would be difficult to determine whether those metrics were improving or declining over time.
For instance: A salesperson is responsible for generating leads but also has another role as an account manager who handles follow-up calls after those leads have been generated. Both roles involve different types of activity so having two different KPIs would be difficult. Using just one KPI may not accurately reflect the true state of either process. Therefore using multiple KPI metrics helps ensure that management has access to relevant information at all times throughout their day-to-day operations.
KPI definitions:
A key performance indicator (KPI) is a measurement of progress toward the achievement of a specific goal. KPIs are used to measure the success or failure, as well as other aspects, of projects, departments, and organizations.
The most common types of KPIs include:
- Revenue targets
- Return on investment (ROI) metrics
- Profit margin percentages
Metrics definition:
Metrics are a way to measure and monitor the performance of a business. Metrics are specific to the business and should be defined before starting any BAM project. Metrics must be defined by the business users, not IT or marketing professionals.
Trigger:
Triggers are used to start and stop the process of monitoring. They can be set up either on a schedule (e.g., once per day) or manually. In addition, triggers can be set up to run asynchronously (i.e., at different times).
Triggers may also run when specific events occur in your system:
- An event notification will be triggered if an email has been sent successfully or failed because of an error condition. E.g., when an email was sent successfully but there was no recipient address stored for that person, this would cause the trigger to fire off an alert about “no recipients”.
- A debug log is generated after each event has occurred. This helps you know what happened during that period without needing any extra information from users who logged into their accounts during those moments. People using the application during that period might notice some changes done by others. Without the debug log, it will become difficult to restore the lost data and keep track of the changes that happened between the events.
Timer:
A timer is a component that measures the time interval between two events. The most common use of timers is to measure the time interval between two events, such as when a user presses the “Start” button and starts running the program. A timer can also be used to measure the time interval between two events in real-time systems (for eg. a game).
Counter:
A counter is a measure of the number of times a specific activity has occurred. It is often used to track the number of times a business process has been executed or the number of times an application has been used.
Monitoring scopes:
Each monitoring scope must be defined before it can be used in BAM. There are two types of monitoring scopes: item level and user level.
- Item Level Monitoring Scope (ILM): This scope defines what items you want to monitor, such as users or transactions. You can use this to track specific events related to an item, like when it was created and last modified, among other things.
- User Level Monitoring Scope (ULM): This scope defines which users will be monitored at all times regardless of whether they are logged into your system or not. This scope will help to understand what data they will have access to when logged in.
Business situations:
Business situations are the context for a business process. They are the environment in which a process occurs, with specific parameters and rules that must be followed. Businesses have several different types of business situations, including:
Financial situation
The financial health of a company depends on its ability to generate revenue from operations and reserve funds for future expansion or growth. A good example is how Walmart uses its balance sheet as a tool to determine when it needs additional capital investment from shareholders or lenders.
Market situation
Competitive pressure can create uncertainty about demand for products or services from competitors. They may be offering similar products at lower prices than yours. This creates an opportunity for you if you can lower prices without losing sales volume (and vice versa).
- For example, if there is too much competition in your industry then you will need more resources like advertising campaigns to let customers know about all available options before making their final purchasing decision!
The BAM offers necessary feedback to help you focus on the important business situations that will improve your business performance and increase your competitive advantage.
Monitoring the archetype:
One of the most important things to remember when designing a business activity monitor is that you must first define the problem before starting on a solution. Goals are only useful if they are specific and measurable. So you must set them before you start working on anything else.
The model that you develop should enhance your monitoring efficiency. Since the whole of the model is made top-down it is necessary to define all the KPIs and metrics.
Interactions and business situations:
Business situations are a set of actions that can be performed by the user. Once the model is designed, KPIs and metrics defined, triggers defined, and actions processed then it’s time to measure the reaction to a specific business situation.
BAM results in visualization:
BAM results visualization is a graphical representation of the information from business activity monitoring. It can be used to find trends and patterns in your data, compare different metrics, and more.
In addition to being a useful tool for managing business activity monitoring data, visualization also helps you understand how your business works by showing you where you are spending money or what resources are being used up most often.
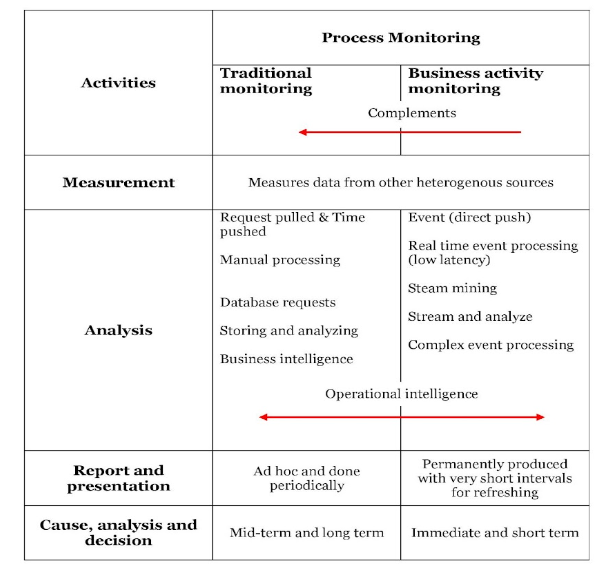
The Relationship between Traditional Process Monitoring and BAM
Traditional process monitoring is driven by time and requests. This can create a significant lag in delivering the results. This is a serious problem as process execution comes with unexpected events which have to be dealt with promptly.
These are the elements of process monitoring and the BAM that you use complements traditional monitoring. The BAM will take up data from other sources and measure its processes. The analysis will be triggered in terms of events and all of this happens in real-time in business activity monitoring. Whereas in traditional process monitoring, the processes are analyzed in terms of requests which are time-based.
In both analyses, operational intelligence plays a major role and complements one another. Finally, the reporting is done permanently and with exceptions in terms of BAM whereas it is Ad hoc in traditional monitoring. In BAM, the actions and decisions are made short term and in traditional monitoring, it is done mid-term or long-term by addressing the top management. You can see how BAM as event-driven is complacent in traditional monitoring.
BAM in a non-process-enabled environment vs BAM in the process-enabled environment
A process-enabled environment is one where processes are applied to all or most of the work that needs to be done to complete a task or project. In this type of environment, every action performed by every member of the team is controlled by a process that has been defined upfront. In a non-process-enabled environment, there are no formalities in place for controlling how an individual performs their job, and there may be many different paths that lead to the completion of a task or project.
The non-process-enabled environment (NPE) is an environment in which a process is not required, such as a physical device that does not have any software applications installed on it. In this type of environment, it is common for teams to work autonomously on their projects and not report back with any information until they are ready.
This lack of process creates problems for everyone involved because it makes it difficult for management to understand what is going on within the team and how best to support it. It also makes it difficult for other departments who might need to rely upon information from the team’s work product (such as marketing).
In the case of a non-process enabled BAM, there are only two methods to achieve the same result – manual and automation. Manual happens when a user interacts with the system manually and does not use any tool or application to automate the process. Automation is achieved using an application or tool that helps a user accomplish their task effectively and efficiently.
In the case of a process-enabled BAM, there are many more ways to achieve the same results. Users can use the system through different applications or tools that help them perform their tasks easier and faster.
For example, if we want to create a new document, then we can use Microsoft Word as our application or tool. This will help us to create documents without having any knowledge about how these documents are created or stored on our system.
Best Business Activity Monitoring Tools
1. Cflow
Cflow as a business activity monitoring software can enhance your business process management. It helps in monitoring and controlling the activities of your company, so you can improve its efficiency.
Cflow can be an integral part of any organization’s workforce management system (WMS) because it allows companies to reduce costs by reducing errors from processes that are not being performed correctly or efficiently. It also helps companies improve their processes through better planning, communication between departments within an organization, and more efficient use of resources such as time/money spent on repetitive tasks or adding new employees when needed.
2. IBM MQ
IBM MQ is a business activity monitoring tool that is used by businesses to monitor their processes and analyze data. It also helps identify trends, identify problems, and make decisions based on the information it provides.
IBM MQ lets you create dashboards that display metrics such as performance and cycle time so you can quickly see how your business is performing. You can also use it to create alerts when certain events occur (like exceeding a set threshold).
3. TIBCO
TIBCO Spotfire is a business activity monitoring software that helps you visualize and analyze your data in real-time. It offers the best way to gain an understanding of your business processes, uncover new insights about customer behavior, and make better decisions.
TIBCO Spotfire Data Analytics has been designed for businesses that need to identify patterns in large volumes of data. You can use it as part of your analytics workflow to discover actionable insights that improve decision-making or drive revenue growth. You can also reduce costs through better workforce productivity and efficiency.
4. Oracle BAM
Oracle BAM is a business activity monitoring tool. It is used to monitor and analyze business processes, transactions, and events. This can be done through the use of metrics that are collected by your system. By using this information, you will be able to identify problems in your business process or performance so that they can be fixed before they become an issue later on down the road. Oracle BAM offers automatic alerts when certain conditions are met or when there is an issue with one of their processes (for example, “low inventory”).
5. Infrared360
Infrared360 is a business activity monitoring tool that enables you to monitor, report, and analyze your business’s performance. It is easy to use and has an intuitive interface that makes it easy for anyone to get started with it.
Infrared360 can be used for real-time monitoring, reporting, and analysis of your organization’s performance data in one single place. The free trial version allows customers to view up to five weeks of activity data from their accounts (no external users are allowed).
6. Aurea CX Messenger
Aurea CX Messenger is an enterprise-grade messaging solution that helps you connect, collaborate, and communicate with your customers, partners, and employees. It is a cloud-based application that provides real-time communications across your organization.
It supports all major communication channels like email, voice mail, chatbot, and video conferencing (Skype for Business).
7. Knowledge Sync
Knowledge Sync is a business process management software that helps you manage your sales and marketing processes. It’s cloud-based, meaning you can access it from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. Knowledge Sync integrates with Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and Microsoft Dynamics GP so that you can use its powerful features to automate data collection at all stages of the buying cycle.
Knowledge Sync’s complete solution for managing business processes includes
- A corporate information system that allows companies to create custom workflows based on specific tasks or steps within their workflow model;
- An integration module for integrating external applications into existing workflows;
- A dashboard tool allowing users to view how their organization is performing against its goals.
There are many business activity monitoring tools available on the market, but some of the best are Cflow, IBM MQ, and Tibco. Each of these businesses has developed a different way to track all of your data in one place and make it easy for you to access it from anywhere.
Know the Benefits of cflow’s Business Activity Monitor
Cflow is a software platform that helps you build personalized business applications. It gives you access to the same powerful features as a full-blown BPM suite but with less overhead and fewer headaches.
Cflow is for users who want more flexibility in how they can use their data, so they built it into something that could work with other tools. This makes it easy to use alongside other software platforms like Salesforce and SAP.
With the information about your business processes at your disposal, it becomes easier for you to make informed decisions.
You will be able to see where improvements are needed and where resources need to be allocated. This allows businesses to identify problems quickly and fix them before they get out of hand.
Businesses that use cflow’s BAM will also be able to see what is working and what is not working based on their data:
- whether or not customers are coming through their doors;
- how often they are using certain products or services;
- how many times people have opted for their products in order for them not only to improve customer service but also to increase profits as well!
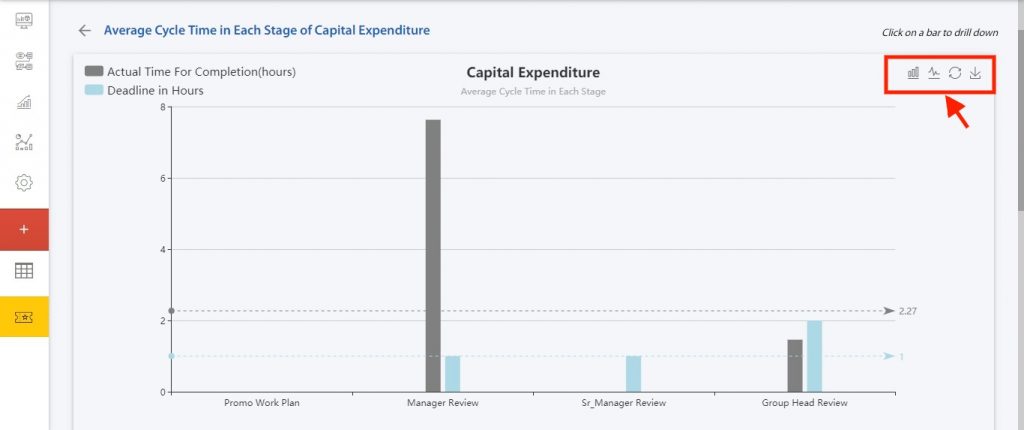
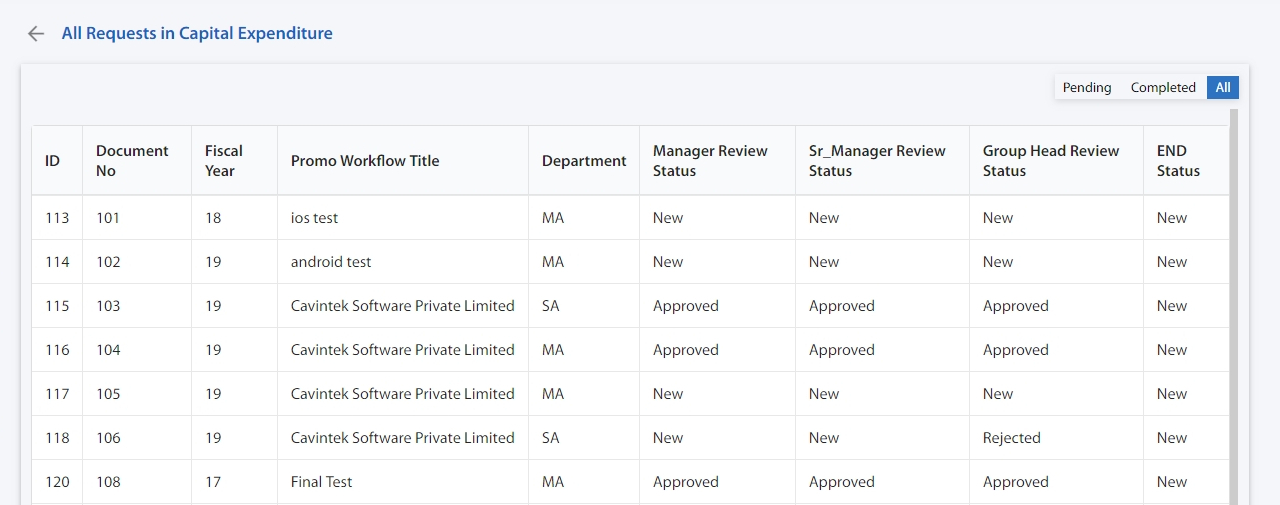
You can gain insight and drive business in your processes by measuring past performance and using a consistent set of metrics. Cflow’s business activity monitor (BAM) can be accessed by selecting the “Analytics” option.
You can see the average cycle time in days which gives the necessary insight into how long the workflows stayed in each stage. The actual time shows the time taken for the request in the approval stage. The deadline in hours denotes the deadline and also the due in each field. The graph can be viewed in lines, bar graphs, and pie charts which can be downloaded and saved for future reference.
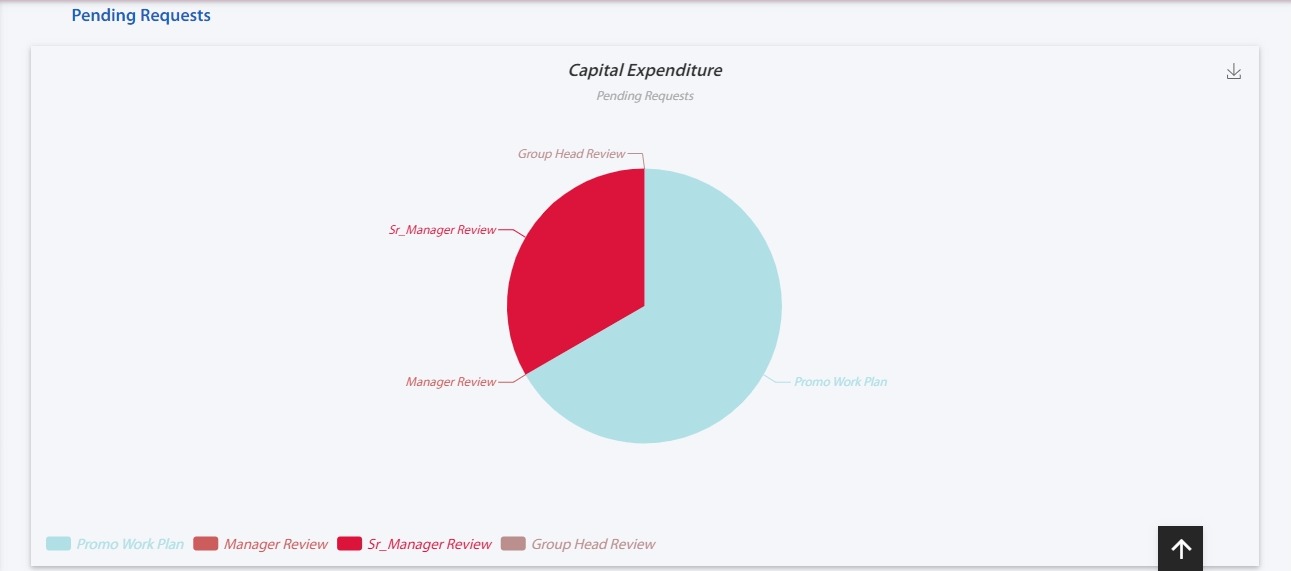
Clicking on the requests will give you a view of the data in the table form showing the date of pending, and completed requests, and all other details in the workflow.
In conclusion, business activity monitoring is a powerful solution to many of today’s business challenges. It can be used to optimize processes and improve the efficiency of your organization. Business activity monitoring helps you gain insight into how well your business is performing, where it needs improvement, and how much time each process takes. BAM allows you to make informed decisions based on real data rather than assumptions about what might happen if certain actions were taken instead.