Procurement and Logistics: Understanding the Connection in Supply Chain Management

Key takeaways
- Procurement and acquisition are often used interchangeably but serve different purposes in business and government operations.
- Procurement focuses on obtaining goods and services through contracts, while acquisition involves a broader process including sourcing, evaluation, and integration.
- Understanding the difference between procurement and acquisition helps streamline operations, reduce costs, and align with strategic goals.
- Both procurement and acquisition play critical roles in supply chain and government project execution.
- Clarifying procurement vs acquisition processes ensures better compliance and operational efficiency.
Procurement and logistics are often viewed as separate components within the supply chain. However, they work closely together to ensure that goods and services flow seamlessly from supplier to end user. Procurement is responsible for sourcing, negotiating, and purchasing, while logistics manages the movement, storage, and delivery of those purchased items. The synergy between these two functions has become increasingly important in today’s complex, global supply chains.
This blog will explore what procurement and logistics mean individually and together, their differences and similarities, the importance of integration, and real-world applications. Whether you’re managing enterprise procurement or overseeing logistics operations, understanding how these functions align is crucial to optimizing the supply chain.
What is Procurement and Logistics?
Procurement refers to the process of identifying, sourcing, negotiating, and acquiring goods or services needed by an organization. It includes supplier selection, contract management, purchasing decisions, and ensuring cost-effectiveness and compliance. Procurement can be direct (for production inputs) or indirect (for administrative or support functions).
Logistics, on the other hand, deals with the physical flow of materials and products. This includes transportation, warehousing, inventory control, order fulfillment, and delivery to the final destination. Logistics ensures that what is procured is received, stored, and moved efficiently through the supply chain.
Together, procurement and logistics represent both the decision-making and execution sides of supply chain operations. Procurement secures the resources, and logistics ensures their timely and accurate delivery.
Table of Contents
Difference Between Procurement and Logistics
While procurement and logistics work together, they have distinct responsibilities and workflows within the supply chain. Understanding these differences is important for business leaders to leverage these functions.
Aspect | Procurement | Logistics |
Core Function | Sourcing and purchasing | Transportation and distribution |
Process Focus | Supplier engagement and cost management | Physical handling and timely delivery |
Key Metrics | Cost savings, supplier performance | Delivery speed, inventory accuracy |
Involves | Contracting, vendor management | Shipping, warehousing, tracking |
Role in Supply Chain | Begins the supply flow | Completes the supply flow |
Understanding the difference between procurement and logistics helps businesses allocate responsibilities appropriately, minimize redundancies, and improve supply chain responsiveness.
Procurement Logistics Process
The procurement logistics process is the structured coordination of sourcing and transportation activities to ensure that goods are delivered efficiently, accurately, and at the right time. It acts as the operational link between purchasing decisions and the physical movement of materials, making it a core component of any modern supply chain.
This process involves multiple steps, right from forecasting demand to receiving goods, each requiring careful planning and collaboration between procurement and logistics teams. When executed effectively, it leads to reduced lead times, optimized inventory, and improved supplier performance.
Demand forecasting and requirement planning
The process begins with identifying what materials, products, or services are needed across departments or production units. Accurate demand forecasting helps procurement teams understand order quantities, reorder points, and the timing of purchases. It also provides logistics teams with visibility into upcoming shipments, enabling them to plan transportation and warehousing accordingly.
Supplier coordination and lead time alignment
Once the requirements are clear, procurement teams engage with suppliers to confirm product availability, delivery timelines, and order volumes. This step is critical in aligning supplier capacity with logistical readiness. If lead times are too long or uncertain, logistics teams may need to adjust transportation modes or hold buffer stock to maintain service levels.
Order placement and documentation
Procurement teams then issue purchase orders, which serve as formal contracts with suppliers. Accurate documentation, including product specifications, quantities, packaging requirements, and delivery terms, is essential at this stage. These details are shared with logistics to prepare for incoming shipments and to ensure that receiving processes are aligned.
Transportation planning and scheduling
Once the supplier confirms shipment readiness, logistics takes over to plan the transportation. This includes selecting the mode of transport (air, sea, rail, or road), booking carriers, and scheduling pick-up and drop-off times. For international shipments, this step also includes coordination of customs documentation and import/export compliance.
Inbound logistics and tracking
As the goods are shipped, logistics teams monitor their movement in real time using tracking systems and freight visibility tools. They coordinate with carriers and suppliers to manage delays, reroute shipments if necessary, and provide updates to procurement teams on estimated delivery times.
Receiving and quality inspection
Upon arrival at the warehouse or destination, goods are received, inspected, and documented. Logistics teams ensure that the correct quantities have been delivered in good condition. Any discrepancies or damages are reported back to procurement for resolution with the supplier. This step may also involve updating inventory systems and triggering payment processes.
Inventory allocation and storage
After inspection, goods are moved to appropriate storage locations or directly to production or sales points. Inventory is updated, and procurement teams are notified of completion. In cases of just-in-time procurement, this step may be bypassed, with goods going straight to the point of use.
Performance review and process optimization
The final step involves reviewing the entire procurement logistics cycle to identify gaps, bottlenecks, or inefficiencies. Metrics such as lead time accuracy, supplier reliability, delivery performance, and cost-effectiveness are analyzed. Insights from this review help refine future procurement decisions and logistics planning.
The procurement logistics process is highly dependent on cross-functional coordination, real-time data sharing, and continuous feedback loops. When designed and executed properly, it supports operational continuity, reduces excess inventory, and enhances supply chain resilience.
Role of Logistics in Procurement
Logistics plays a critical role in supporting procurement objectives by ensuring the timely and cost-effective delivery of purchased items. Without a reliable logistics network, even the best procurement strategies can fail due to delayed shipments, damaged goods, or incorrect deliveries.
In procurement, logistics helps with:
- Coordinating with suppliers on shipment schedules and packaging specifications.
- Planning transportation modes to balance cost and delivery timelines.
- Managing import/export documentation and customs procedures for international sourcing.
- Enabling just-in-time inventory systems by optimizing delivery frequencies.
- Providing data that supports vendor performance evaluation based on delivery reliability.
When logistics teams work closely with procurement, they can jointly negotiate better delivery terms and reduce total landed costs, leading to improved supply chain efficiency.
Procurement and Logistics Management
Managing procurement and logistics together requires a cross-functional approach. Organizations that treat these functions as separate silos often face bottlenecks, miscommunications, and avoidable expenses. Integrated procurement and logistics management focuses on coordination across sourcing, transport, storage, and delivery to achieve end-to-end visibility and efficiency.
Key practices in procurement and logistics management include:
- Developing centralized platforms that link purchase orders with logistics workflows.
- Using real-time tracking systems to monitor the movement of procured goods.
- Creating shared performance metrics that evaluate suppliers and carriers together.
- Forecasting demand accurately to align procurement schedules with delivery capacities.
- Engaging in collaborative planning with suppliers and logistics providers.
An integrated approach enables better decision-making and reduces disconnects between purchasing decisions and delivery realities.
Procurement Logistics and Supply Chain
Procurement and logistics are foundational pillars in the broader supply chain. Procurement determines what is brought into the organization, while logistics ensures it reaches where it is needed, on time and in good condition. Together, they directly influence supply chain performance, including production timelines, customer service levels, and cost structures.
In modern supply chains, procurement logistics plays a key role in managing supplier risks, responding to global disruptions, and optimizing end-to-end inventory. For example, sourcing components from overseas requires procurement teams to consider shipping lead times, customs delays, and warehouse space, all of which fall under logistics coordination.
Supply chains that align procurement logistics with production and distribution strategies can maintain higher agility, reduce stockouts, and enhance overall competitiveness.
Importance of Procurement and Logistics
The importance of procurement and logistics lies in their combined impact on operational continuity and customer satisfaction. When procurement sources high-quality goods at competitive prices, and logistics ensures those goods arrive promptly and safely, the organization is better positioned to meet market demands.
Poor coordination between these two functions can result in production delays, increased costs, and lost sales opportunities. On the other hand, when procurement and logistics are well-aligned, companies benefit from lower total costs, improved delivery performance, and stronger supplier relationships.
This integration is especially crucial in industries like manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and construction, where materials availability directly impacts service delivery or project timelines.
Integration of Procurement and Logistics
Integrating procurement and logistics is no longer optional, but an absolute competitive necessity. With increasing complexity in global sourcing and heightened customer expectations, organizations must ensure that purchasing decisions and delivery capabilities are tightly synchronized.
Key enablers of integration include:
- Shared digital platforms that link procurement and logistics teams.
- Unified supplier and carrier performance dashboards.
- Collaborative planning meetings to align forecasts and delivery schedules.
- Data analytics for better visibility into procurement lead times and logistics bottlenecks.
- AI-driven tools for optimizing order quantity, delivery windows, and cost.
The integration of procurement and logistics leads to faster decision-making, better inventory management, and more resilient supply chain operations.
Procurement Logistics Strategy
A procurement logistics strategy is a coordinated approach that aligns sourcing decisions with logistics operations to ensure that purchased goods and services are delivered in a timely, cost-effective, and efficient manner. It bridges the gap between procurement planning and logistical execution, allowing organizations to minimize delays, reduce costs, and increase supply chain responsiveness.
Developing a robust procurement logistics strategy starts with a deep understanding of the organization’s procurement patterns, supplier capabilities, transportation infrastructure, and demand variability. The goal is to not only secure the best products at competitive prices but also ensure that these products arrive when and where they are needed without incurring unnecessary expenses or causing operational disruptions.
Selecting suppliers based on logistics capabilities
Traditional procurement strategies often prioritize price and quality. However, a modern procurement logistics strategy places equal emphasis on a supplier’s ability to deliver consistently and quickly. Suppliers must be evaluated not only on their cost proposals but also on their proximity to production sites, shipping lead times, warehouse availability, and flexibility to handle urgent orders.
Focusing on total landed cost
Instead of focusing solely on purchase price, a comprehensive procurement logistics strategy considers the total landed cost. This includes the product cost, shipping charges, customs duties, taxes, handling fees, insurance, and storage expenses. By evaluating the complete financial impact, companies can make more informed sourcing decisions that reflect true profitability.
Establishing flexible delivery schedules
Procurement logistics strategies must account for variability in demand and external factors like supply disruptions or seasonal peaks. Establishing flexible delivery windows, buffer stock, and agreements for expedited shipping allows companies to adjust quickly without halting operations. Flexibility helps avoid overstocking and understocking while keeping costs under control.
Building diversified supplier and carrier networks
Relying on a single supplier or logistics provider creates risk. A resilient strategy involves developing a diversified network of local and global suppliers, as well as multiple shipping partners. This provides options in the event of geopolitical disruptions, port congestion, or supplier insolvency, ensuring continuity in supply and delivery.
Leveraging data and automation for decision-making
Procurement logistics strategies today are heavily driven by data. Organizations use analytics tools to forecast demand, assess supplier performance, and track shipping costs. Automation platforms can connect procurement systems with logistics operations, enabling real-time tracking of orders, proactive alerts for delays, and dynamic route optimization.
Sustainability and ethical sourcing considerations
An effective procurement logistics strategy also factors in environmental and social responsibility. Sourcing from environmentally conscious suppliers, using fuel-efficient transportation methods, and reducing packaging waste are all elements that align with broader corporate sustainability goals and regulatory expectations.
In summary, a well-developed procurement logistics strategy enables organizations to integrate sourcing and delivery into a cohesive framework. It helps balance cost, speed, quality, and risk, empowering businesses to build agile, scalable, and resilient supply chains capable of adapting to evolving market demands.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
Functions of Procurement and Logistics
Procurement and logistics are not isolated tasks but are made up of several interrelated functions that work together to drive an efficient supply chain. Understanding each function helps organizations assign responsibilities, improve process efficiency, and optimize performance across sourcing and delivery operations.
Procurement Functions
Identifying needs across departments
Procurement begins with recognizing the requirements of various departments within the organization, irrespective of whether it’s raw materials for production, software for IT teams, or office supplies for administration. This function ensures that purchases are aligned with operational goals and that the right items are acquired in the right quantity at the right time.
Supplier identification and selection
Once the needs are identified, the procurement team evaluates potential suppliers based on criteria such as cost, quality, reliability, delivery capacity, and compliance with regulations. This function involves pre-qualification, supplier scoring, and vetting processes to ensure the chosen vendor can meet expectations.
Price negotiation and contract management
Procurement professionals are responsible for negotiating prices, payment terms, and delivery schedules to ensure cost-effectiveness. They also draft and manage contracts that outline legal obligations, performance standards, penalties for non-compliance, and renewal terms. Effective negotiation and contract management help minimize financial risk and ensure mutual accountability.
Managing purchase orders and approvals
Once a supplier is selected, procurement teams generate and track purchase orders. This includes routing the order for internal approvals based on company policy, ensuring that budget limits and authorization levels are met before finalizing the order. This function promotes transparency and avoids unauthorized spending.
Ensuring regulatory and budget compliance
Procurement teams must operate within internal financial guidelines and comply with external regulations, especially when dealing with government contracts or international suppliers. This function involves tracking spend against allocated budgets, maintaining audit trails, and ensuring ethical sourcing practices.
Logistics Functions
Planning and executing transportation
Logistics teams are responsible for planning how goods will be transported, by road, air, rail, or sea, based on cost, urgency, and destination. This function includes selecting carriers, optimizing shipping routes, and scheduling pickups and deliveries to align with procurement and production timelines.
Managing warehousing and inventory
Efficient logistics depends on proper storage and inventory control. This function includes receiving goods, storing them in optimal conditions, managing inventory levels, and implementing warehouse management systems. Effective warehousing reduces damage, spoilage, and stockouts while ensuring availability when needed.
Order fulfillment and last-mile delivery
Logistics plays a key role in ensuring that customer orders are picked, packed, and shipped accurately and on time. This function extends to last-mile delivery, the final leg of the shipment journey to the customer, which has a major impact on customer satisfaction and retention.
Monitoring shipment status and resolving delays
Tracking and monitoring the movement of goods in transit is crucial for maintaining visibility and control. This function includes using GPS tracking, shipment notifications, and exception management to resolve issues like route deviations, customs delays, or weather disruptions before they impact operations.
Maintaining accurate records for audits and KPIs
Logistics teams must maintain detailed records of all shipments, deliveries, inventory movements, and transportation costs. These records support financial audits, ensure regulatory compliance, and provide performance data for logistics KPIs such as on-time delivery rate, cost per shipment, and inventory turnover.
Together, these functions of procurement and logistics form the backbone of a responsive and resilient supply chain. By ensuring that sourcing decisions and delivery execution are tightly aligned, organizations can reduce costs, improve service quality, and maintain a competitive advantage.
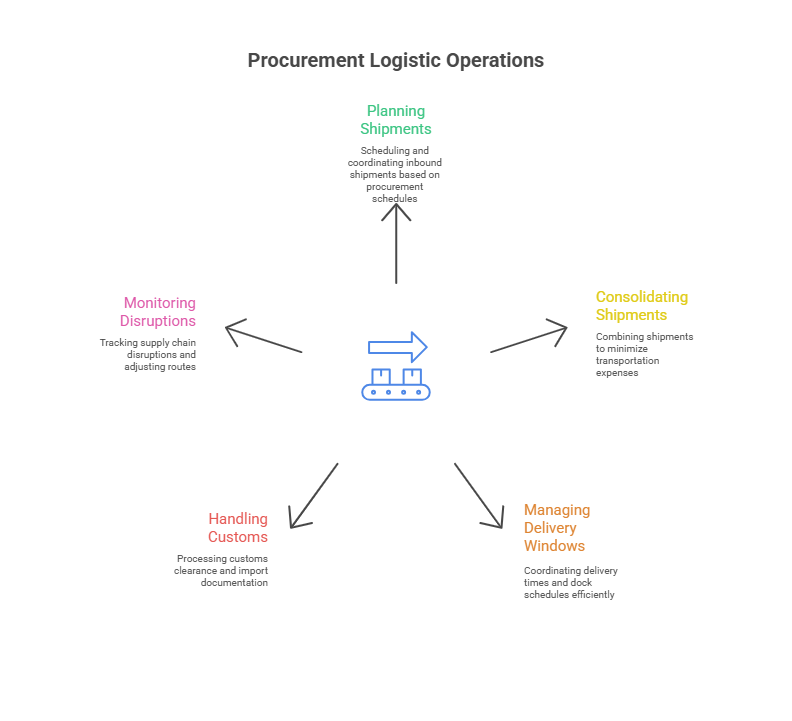
Procurement Logistics Operations
Procurement logistics operations focus on the coordination between what is being purchased and how it is moved through the supply chain. These operations involve collaboration between buyers, suppliers, freight forwarders, and warehouse managers.
Key elements of procurement logistics operations include:
- Planning inbound shipments based on procurement schedules
- Consolidating shipments to reduce transportation costs
- Managing delivery windows and dock scheduling
- Handling customs clearance and import documentation
- Monitoring supply disruptions and re-routing as needed
By aligning logistics operations with procurement plans, organizations can streamline inbound flows, reduce inventory costs, and ensure production continuity.
Final Thoughts
Procurement and logistics are two vital components of a high-performing supply chain. While procurement ensures that goods and services are sourced correctly, logistics guarantees their timely and efficient delivery. The coordination between these functions drives business efficiency, reduces costs, and strengthens customer satisfaction.
A platform like Cflow helps organizations automate and integrate procurement and logistics workflows using no-code automation. From purchase approvals to shipment tracking, Cflow enables real-time visibility, faster processing, and fewer manual errors. Sign up for Cflow to bring clarity and control to your procurement and logistics operations.
FAQs
What are procurement and logistics in supply chain management?
Procurement involves sourcing and purchasing goods, while logistics manages the storage, transport, and delivery of those goods within the supply chain.
How are procurement and logistics related?
Procurement and logistics are interdependent; procurement secures the goods, and logistics ensures they are delivered where and when needed.
What is the difference between procurement and logistics?
Procurement focuses on supplier selection and purchasing, while logistics handles the physical movement and storage of materials.
Why is integrating procurement and logistics important?
Integration improves supply chain visibility, reduces lead times, and prevents bottlenecks between purchasing decisions and delivery execution.
What are procurement logistics operations?
These are the activities that coordinate delivery schedules, transportation, and warehousing to support the procurement process effectively.
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business:

Do better workflow automation with Cflow
Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms, etc. to save time and cost.

Talk to a workflow expert
Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize your daily tasks.

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master workflow automation.